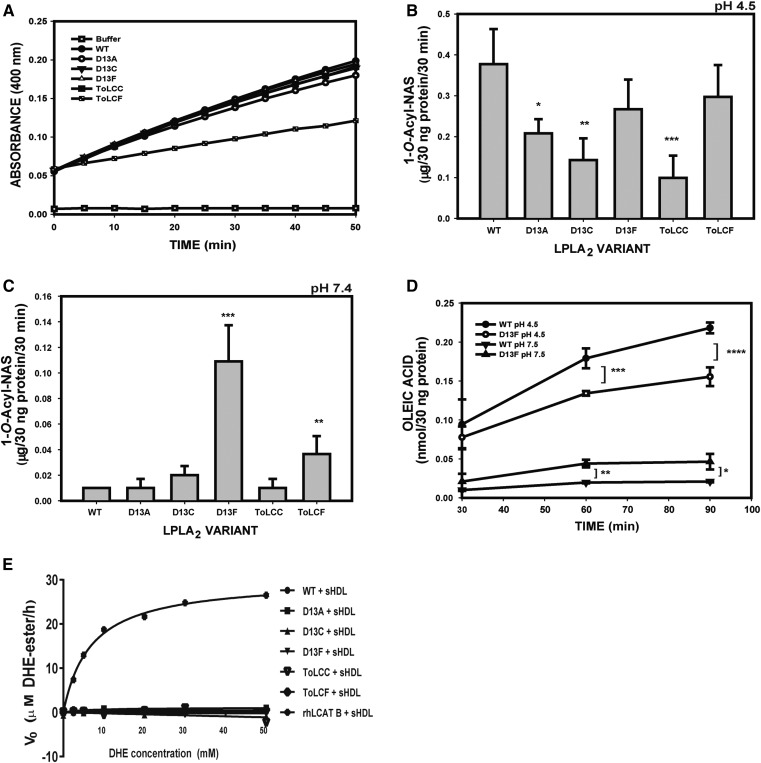
Fig. 2.
Functional characterization of LPLA2 variants. A: Esterase activity measured with pNPB at pH 7.4 of WT and LPLA2 variants. Transacylase activities of LPLA2 were determined using DOPC/sulfatide/NAS liposomes (10:1:3 molar ratio) in 48 mM Na citrate pH 4.5 (B) or in 50 mM HEPES pH 7.4 (C), and incubated with 30 ng protein of each variant for 30 min at 37°C. The HPTLC plates were developed in a solvent system consisting of chloroform /acetic acid 9/1 v/v). Ceramide standards were used to calculate activity. D: Lipase activity of LPLA2. The reaction mixture employed liposomes consisting of DODPC and DOPC (molar ratio, 2.4:1) in 50 mM Na citrate pH 4.5 or 50 mM HEPES pH 7.4. The reaction was initiated by adding 30 ng protein of LPLA2 variant to a final volume of 500 μl for different times at 37°C. The mean activities were expressed as nmol oleic acid/30 ng of protein. E: LCAT activity of rhLCAT and LPLA2 variants. Sterol esterification activity was measured using DHE in combination with cholesterol oxidase. The values for all graphs represent the mean ± SD (n = 3) per time point, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.