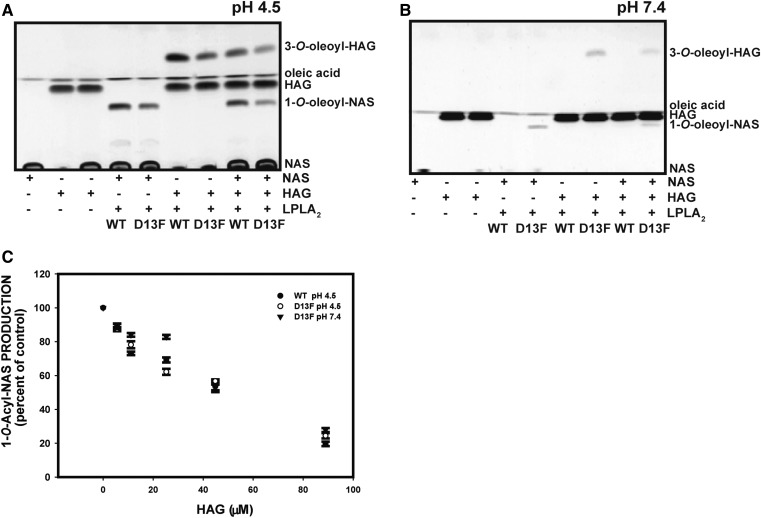
Fig. 7.
Acylation of lipophilic alcohols by LPLA2. A: The formation of 3-O-acyl-HAG (1-O-hexadecyl-2-acetyl-3-oleoyl-sn-glycerol) and 1-O-acyl-NAS by WT and D13F LPLA2 at pH 4.5 were compared. The reaction mixtures consisted of 48 mM Na-citrate (pH 4.5), LPLA2 (30 ng), and liposomes consisting of DOPC, sulfatide, and acceptor (NAS, HAG, or NAS and HAG) with a molar ratio of 10:1:3.25 and in a total volume of 500 µl After the incubation, the lipids were extracted, applied to an HPTLC plate, and developed in a solvent system consisting of chloroform/acetic acid 96/4, v/v. B: The formation of 3-O-acyl- HAG and 1-O-acyl-NAS by WT and D13F LPLA2 at pH 4.5 and 7.4 were compared. The reaction mixture was the same as in A except for the use of HEPES buffer (50 mM) and 60 ng of enzyme. C: The concentration dependent inhibition of 1-O-acyl-NAS by HAG. The graph values represent the mean ± SD (n = 3) per time point using a t-test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.