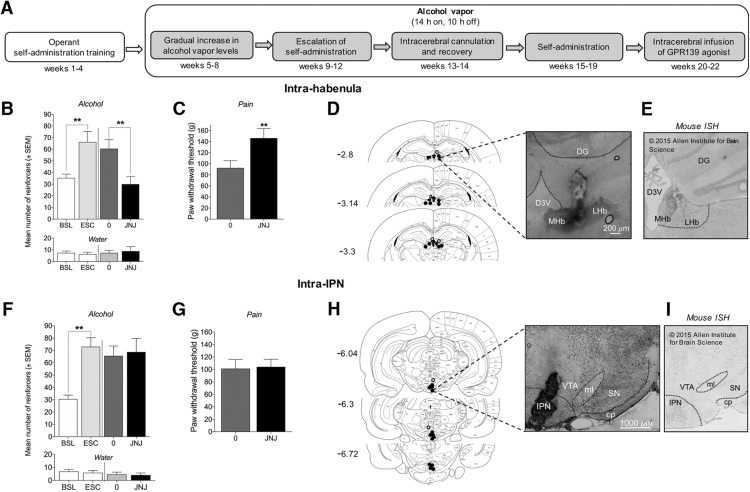
Figure 6.
Intra-habenular but not intra-IPN JNJ-63533054 administration decreases alcohol intake and increases paw withdrawal thresholds in alcohol-dependent rats during withdrawal. A, Timeline of microinfusions of JNJ-63533054 in alcohol-dependent rats. B, Intra-habenular infusion of JNJ-63533054 (0.25 µg/0.5 µl) decreased alcohol self-administration in dependent rats (**p < 0.01), without affecting water self-administration (n = 6). C, Intra-habenular infusion of JNJ-63533054 increased paw withdrawal thresholds during alcohol withdrawal (**p < 0.01). D, Histology of accurate injection sites in the habenula (black circles) and misplaced injection sites (white circles); 5× magnification. E, In situ hybridization of GPR139 receptors in mouse habenula. Modified from Allen Mouse Brain Atlas (AllenMouseBrainAtlas, 2004). F, Intra-IPN infusion of JNJ-63533054 did not affect alcohol or water self-administration in alcohol-dependent rats (n = 7). G, Paw withdrawal thresholds during alcohol withdrawal were unaffected by intra-IPN infusion of JNJ-63533054. H, Histology of accurate injection sites in the IPN (black circles) and misplaced injection sites (white circles); 2.5× magnification. I, In situ hybridization of GPR139 receptors in the mouse IPN. Modified from Allen Mouse Brain Atlas (AllenMouseBrainAtlas, 2004). cp, cerebral peduncle; DG, dentate gyrus; D3V, dorsal third ventricle; LHb, lateral habenula; MHb, medial habenula; ml, medial lemniscus; SN, substantia nigra; VTA, ventral tegmental area.