Fig. 5.
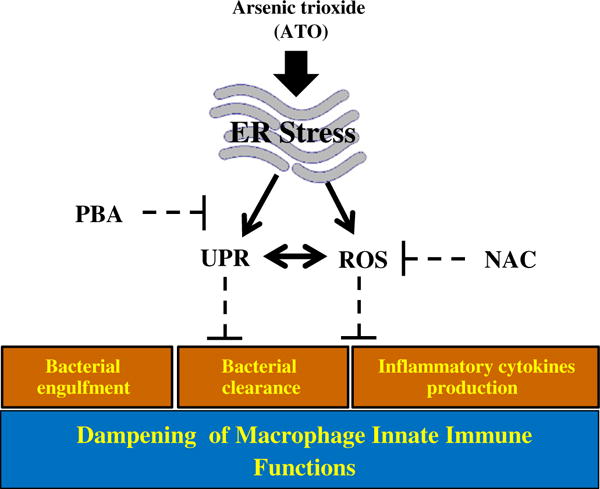
Arsenic treatment impaired macrophage functions are UPR regulated: ATO which causes endoplasmic reticulum stress, induces UPR signaling and ROS concomitantly in macrophage. In addition, ATO-treated macrophage show impairment in innate immune functions including diminished phagocytosis of FITC-labeled latex beads, impaired clearance of phagocytosed fluorescent bacteria and reduced secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines. However, treatment of macrophage with a chemical chaperon, 4-phenylbutyric acid attenuated both UPR signaling and ROS generation in these cells. Furthermore, this treatment afforded significant protection against ATO-mediated impairment of macrophage functions. Similar protective effects against ATO-mediated impairment in innate immune functions were noted following treatment of these cells with antioxidant NAC. Interestingly the mechanism by which NAC affords protection against immunotoxicity of ATO also involves diminution in UPR signaling pathway.
