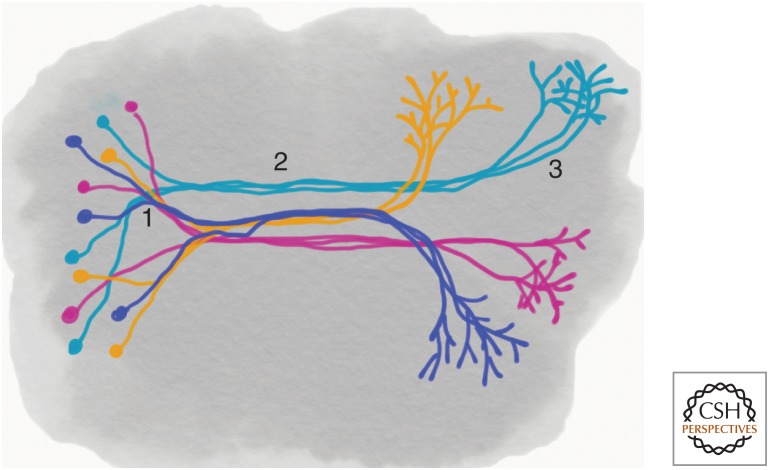
Figure 2.
Potential roles for cadherins in long range neural connectivity. Protocadherins, cadherins, and other adhesion molecules participate in selective fasciculation. (1) Axons expressing a common cadherin or protocadherin sort during elongation through contact-dependent promotion of growth cone motility. (2) Within tracts, axons segregate, as a result of homophilic interactions. This provides an underlying organization to fascicles that are densely populated with a large diversity of axons. Much of axon guidance is mediated by pioneer growth cones responding to arrays of both short- and long-range cues, and occurs when the nervous system is relatively simple. Follower growth cones extend along existing axons, relying heavily on selective adhesion. (3) Homophilic interactions promote target recognition and axonal arborization within the target area. This coarse targeting can be further refined by Ephrin gradients or other guidance cues.