Figure 2.
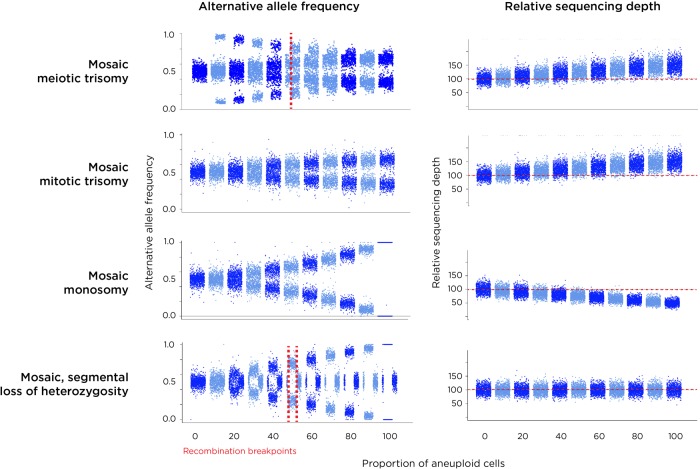
Results of simulations of each of the types of aneuploidy (plus copy number neutral loss of heterozygosity, cnnLOH). Each plot on the left shows the AAF distributions in steps of 10% proceeding from no aneuploidy (complete diploidy) to aneuploidy in all cells. On the right is shown the expected change of sequencing depth for the affected chromosome. Because meiotic trisomy with recombination creates a non-recombined region with LOH and a recombined area with three different haplotypes, two patterns are created within these chromosomes, the pattern in the recombined region being very distinctive (top). The coverage for a trisomic chromosome is increased relative to others in the genome. Trisomy occurring in mitosis (or in meiosis without recombination) generates a similar profile in terms of AAF to mosaic monosomy, but these events are distinguished by coverage being higher for trisomy and lower for monosomy. Segmental cnnLOH is shown in the bottom panels, the affected area of the chromosome showing an AAF pattern similar to monosomy but with no change in copy number. A region showing nonmosaic (100%) cnnLOH reflects consanguinuity, at a locus of identity by descent.