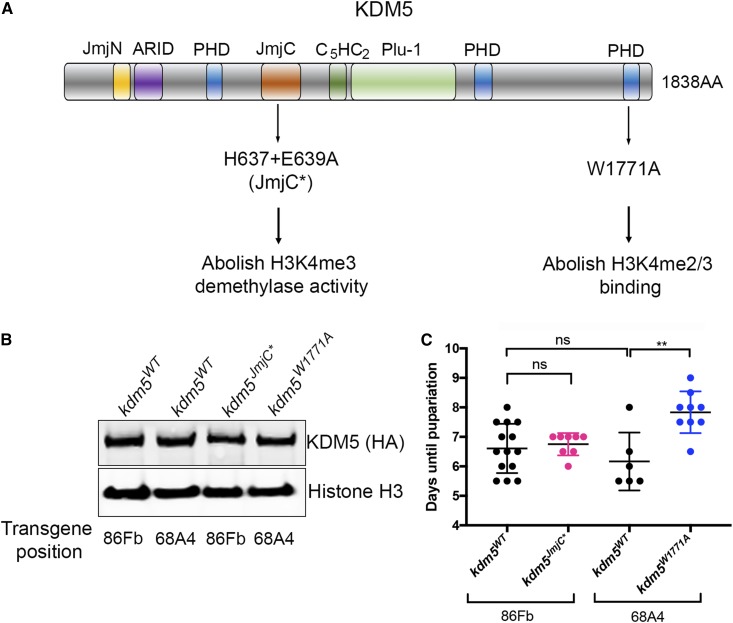
Figure 3.
KDM5-mediated developmental delay is independent of its H3K4me3 removal or binding activities. (A) Schematic of the KDM5 protein showing the domain structure and the location of the JmjC* point mutations that abolish demethylase activity and the W1771A point mutation in the C-terminal PHD motif that prevents binding to H3K4me2/3 (Li et al. 2010). The kdm5JmjC* genomic transgene is inserted at the attP site at 86Fb while the kdm5W1771A transgene is located at the attP site at 68A4. Each mutant strain therefore has a separate control kdm5WT strain with a matching insertion of the wild-type kdm5 genomic region. (B) Western blot showing wild-type expression of KDM5 (using anti-HA; top) in kdm5JmjC* and kdm5W1771A wing imaginal discs. The kdm5WT strain at 86Fb is a control for kdm5JmjC* while the wild-type insertion at 68A4 is the control for kdm5W1771A. (C) Time for 50% of kdm5WT (86Fb; N = 415; 6.9 days), kdm5JmjC* (86Fb; N = 66; 6.75 days), kdm5WT (68A4; N = 379; 6.2 days), and kdm5W1771A (68A4; N = 126; 8.25 days) to pupariate (T1/2). Each data point represents animals counted from an independent cross. N values represent the total number of animals scored. ** P = 0.002.