Figure 6. Structural disorder in LOXL1.
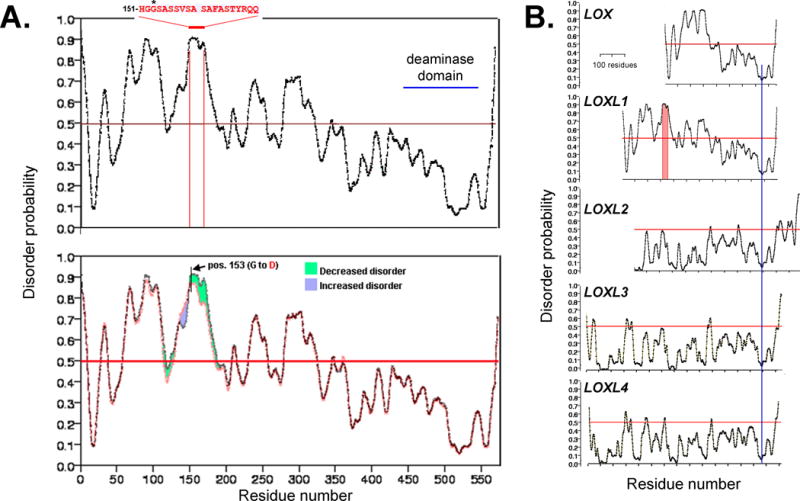
A. LOXL1 contains multiple disordered domains on its N-terminus. Particularly significant is a wide peak of disorder in the 151-170 amino acid domain. It includes the highest risk allele for XFG where homozygosity for glycine (G) at position 153 is associated with 98% of the XFG cases in a broad ethnic diversity USA population 56. The site of copper binding (site of deaminase activity) is indicated. B. Replacement of glycine by aspartic acid (D) at pos. 153 results in a ~ 8-10 % decrease in disorder probability in the 151-180 residue span. C. Comparison of disorder probability for the LOX family of proteins shows domains with high probability disorder exist only in the much smaller LOX protein; LOXL2-4 appear to be highly structured proteins. All sequences have been aligned using a preserved domain of very low disorder probability present at the C-terminus (blue line).
