Figure 1. Connection between schizophrenia (SCZ) risk genes and antipsychotic drug targets.
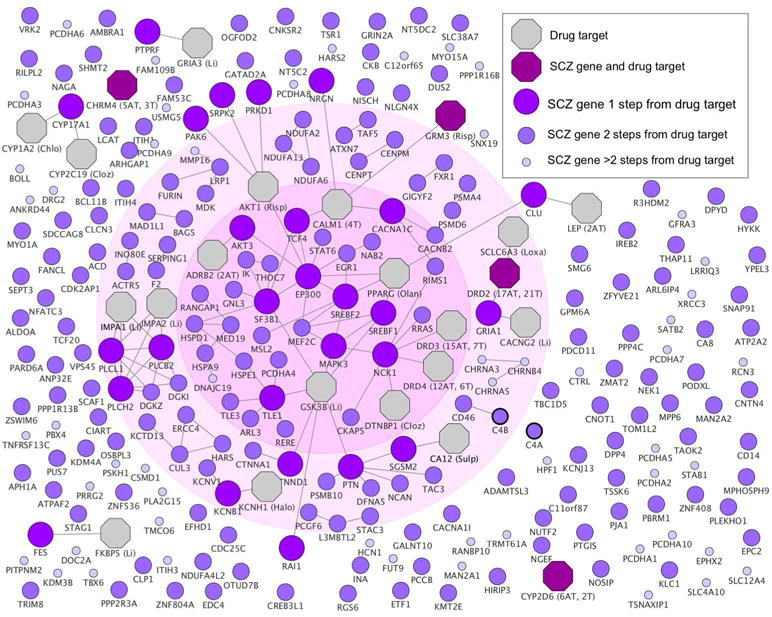
Schizophrenia risk genes are color labeled and sized according to their shortest path lengths to antipsychotic drug targets. Antipsychotic drug targets are shown as octagons, with number of atypical (AT) and typical (T) antipsychotics in parenthesis. Drug targets that do not interact with any risk gene are not shown. Abbreviated drug names are given for proteins that are targeted by a single antipsychotic: Chlo=Chlorpromazine, Cloz=Clozapine, Li=Lithium, Loxa=Loxapine, Olan=Olanzapine, Risp=Risperidone, Sulp=Sulpiride. The inner circle indicates the genes belonging to the largest connected component and the outer circle indicates the interconnected risk genes. We refer to these two gene set components as the core disease module, given that they are used as network properties to quantify the degree to which disease risk genes cluster in specific interactome neighborhoods. Risk genes close to antipsychotic drug targets were significantly overrepresented among interconnected risk genes (p=0.00023) (χ2 test) (counts shown in Supplementary Table 4). For full details of specific antipsychotics targets, see Supplementary Table 3. Further details on C4A and C4B (marked with thicker borders) are shown in Supplementary Figure 2.
