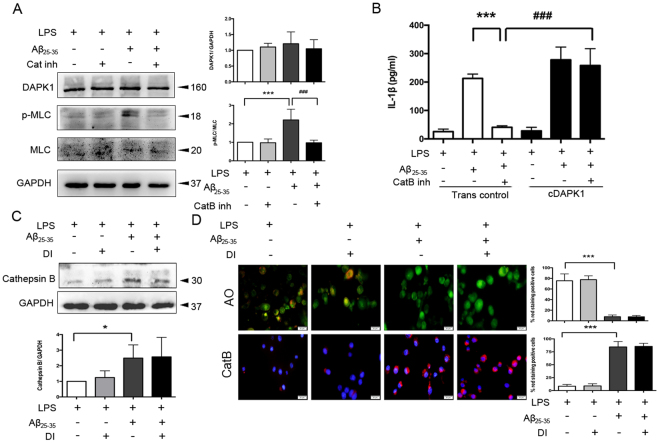
Figure 5.
Aβ25–35-induced cathepsin B acts upstream of DAPK1. (A) The effects of cathepsin B inhibitor (5 μM) treatment on the expression of DAPK1 and p-MLC in LPS-primed, Aβ25–35-stimulated Bv2 cells were analyzed by western blotting analysis (see original blots in Supplementary Fig. S5A). (B) Cells were transiently transfected with DAPK1 overexpression plasmids (cDAPK1) or empty plasmids (Trans control) using Lipofectamine 2000. The effect of cathepsin B inhibitor (5 μM) treatment on Aβ25–35-induced IL-1β secretion in DAPK1 overexpression cells were analyzed by ELISA. (C–D) LPS-primed Bv2 cells were treated with or without DAPK1 inhibitor (10 μM), followed by Aβ25–35 exposure for 24 h. (C) The expression of cathepsin B in the cytoplasm was determined by western blotting analysis (see original blots in Supplementary Fig. S5B). (D) Fluorescent images of acridine orange and a cathepsin B substrate were exemplified (12 images per condition). Scale bar = 20 μm. Data are shown as mean ± SEM for at least three independent experiments. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001; ###P < 0.001. AO: acridine orange; Cat B: cathepsin B substrate; Cat B inh: cathepsin B inhibitor; cDAPK1: constructively activated DAPK1 (DAPK1ΔCaM mutant); DI: DAPK1 inhibitor; Trans con: transfection control.