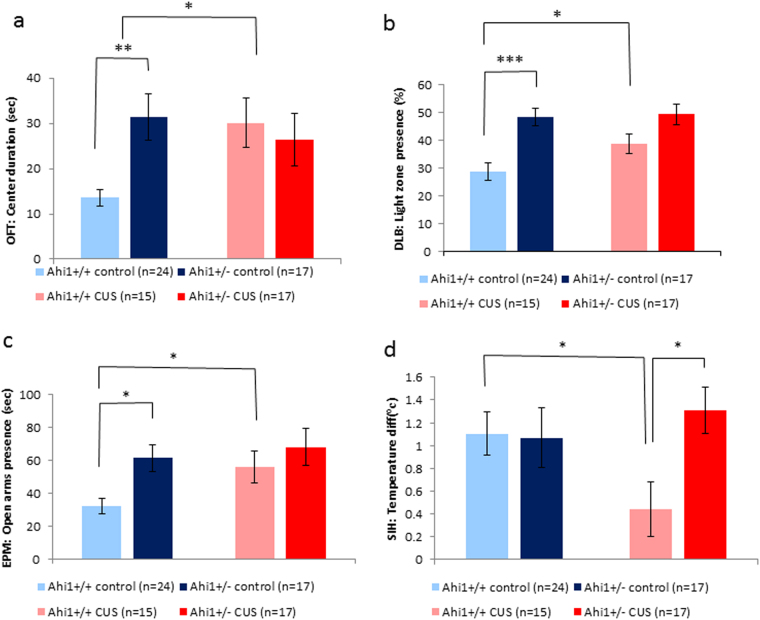
Fig. 2. Effect of CUS on anxiety.
a Effect of CUS on time spent in the center of the open field. Two way ANOVA revealed a significant genotype by CUS interaction (F[1,70] = 6.08, p = 0.016. Post hoc comparisons of simple main with Bonferroni correction effects indicated a significant difference between Ahi1+/+ and Ahi1+/− control mice (p < 0.005), and between CUS-exposed Ahi1+/+ and Ahi1+/+ controls (p < 0.01), but not between CUS-exposed Ahi1+/− and Ahi1+/− controls. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.005; b Effect of CUS on light-dark box preference. Significant main effect of genotype was detected on two-way ANOVA (F[1,70] = 20.18, p = 0.00003), indicating that Ahi1+/− mice spent longer in the open area of the dark-light box than Ahi1+/+ mice. Post hoc comparisons of simple main effects with Bonferroni correction revealed that Ahi1+/− control mice spent longer in the light zone than Ahi1+/+ controls (p < 0.0001), and CUS-exposed Ahi1+/+ mice spent longer in the light zone than Ahi1+/+ controls (p < 0.05), suggesting that the CUS protocol decreased the anxiety of these mice. No such effect was observed in CUS-exposed Ahi1+/− mice. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.0001; c Effects of CUS on time spent in the open arms of the elevated plus maze. Significant main effect of genotype (F[1,70] = 6.869, p = 0.011) on two-way ANOVA, indicating that Ahi1+/− mice spent longer in the open arms of the elevated plus maze than Ahi1+/+ mice, suggesting reduced anxiety of these mice. Post hoc comparisons of simple main effects with Bonferroni correction indicated that Ahi1+/− mice spent longer in the open arms compared to Ahi1+/+ controls (p < 0.01), and that CUS-exposed Ahi1+/+ mice spent longer in the open arms compared to Ahi1+/+ controls (p < 0.05). No similar effect was observed in the CUS-exposed Ahi1+/− mice. *p < 0.05 d Effect of CUS in the stress-induced hyperthermia test. Two-way ANOVA revealed a significant main effect of genotype (F[1,63] = 4.203, p = 0.045), indicating that Ahi1+/+ mice manifested attenuated hyperthermia. CUS blunted hyperthermia in Ahi1+/+ mice, but had no effect on Ahi1+/− mice, reflected in a significant CUS by genotype interaction (F[1,63] = 5.001, p = 0.029). Post hoc tests of simple main effects with Bonferroni correction indicated that CUS-exposed Ahi1+/+ mice displayed a blunted response to acute stress compared to both CUS-exposed Ahi1+/− mice (p < 0.05) and Ahi1+/+ controls (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference between CUS-exposed Ahi1+/− mice and Ahi1+/− control mice. *p < 0.05