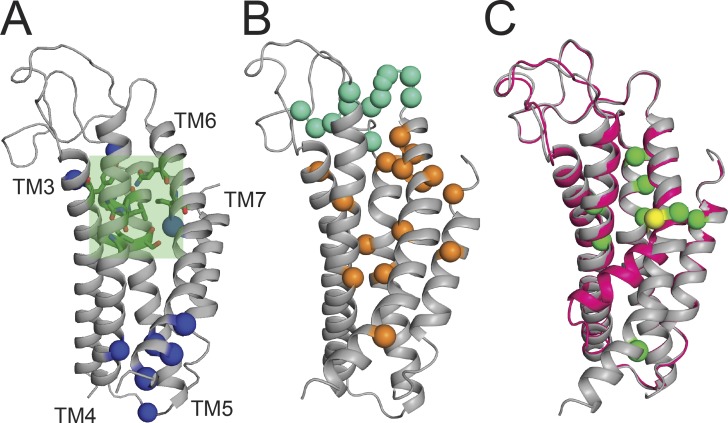
Figure 3.
The mTMEM16A pore. (A) Close-up view of the mTMEM16A pore. Basic residues lining the pore are shown as blue spheres, the neck constriction region is shown as a green shaded area, and key residues are shown as green sticks (Paulino et al., 2017a). (B) Residues important for ion permeation and selectivity: positions within the pore are shown as orange spheres; positions outside the pore that play a role in permeation are shown in cyan (Yu et al., 2012; Dang et al., 2017; Paulino et al., 2017a,b). (C) Structural alignment of the Ca2+-bound structure of mTMEM16A (gray) with the zero-Ca2+ structure (pink). TM6 bends into the pore around G644, shown as a yellow sphere. Green spheres are residues important for Ca2+ gating (Dang et al., 2017; Paulino et al., 2017a).