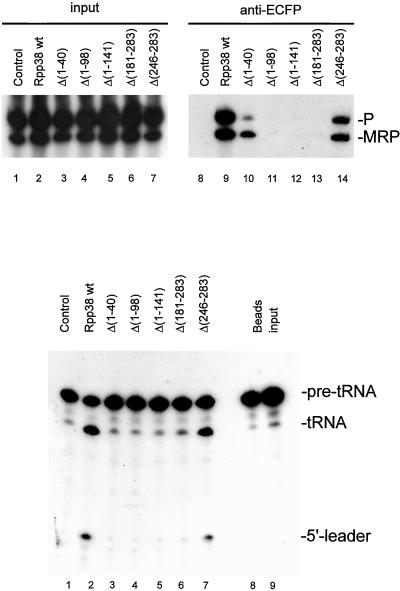
Figure 4.
Association of ECFP-Rpp38 (mutants) with RNase MRP and RNase P ribonucleoprotein particles and RNase P activity associated with ECFP-Rpp38 deletion mutants. (A) Constructs encoding (deletion mutants of) ECFP-Rpp38 were transiently transfected in HEp-2 cells. Extracts from these cells used for immunoprecipitations with anti-ECFP antibodies. RNA isolated from total cell extracts (lanes 1–7) and immunoprecipitates (lanes 8–14) was analyzed by Northern blot hybridization with the use of riboprobes specific for RNase MRP and RNase P RNA. Lanes 1 and 8: material from control cells expressing ECFP alone; lanes 2 and 9: ECFP-Rpp38; lanes 3 and 10: ECFP-Rpp38 Δ(1–40); lanes 4 and 11: ECFP-Rpp38 Δ(1–98); lanes 5 and 12: ECFP-Rpp38 Δ(1–141); lanes 6 and 13: ECFP-Rpp38 Δ(181–283) and lanes 7 and 14, ECFP-Rpp38 Δ(246–283). The positions of RNase P and RNase MRP RNA are indicated. (B) RNase P activity assay associated with anti-ECFP immunoprecipitates from extracts of cells transiently transfected with ECFP-Rpp38 (deletion mutants). Lane 1: material from control cells expressing ECFP alone; lane 2: ECFP-Rpp38; lane 3: ECFP-Rpp38 Δ(1–40); lane 4: ECFP-Rpp38 Δ(1–98); lane 5: ECFP-Rpp38 Δ(1–141); lane 6: ECFP-Rpp38 Δ(181–283); lane 7: ECFP-Rpp38 Δ(246–283); lane 8: beads alone; and lane 9, substrate RNA. On the right, the positions of the pre-tRNA, the mature tRNA and the 5′-leader are indicated.