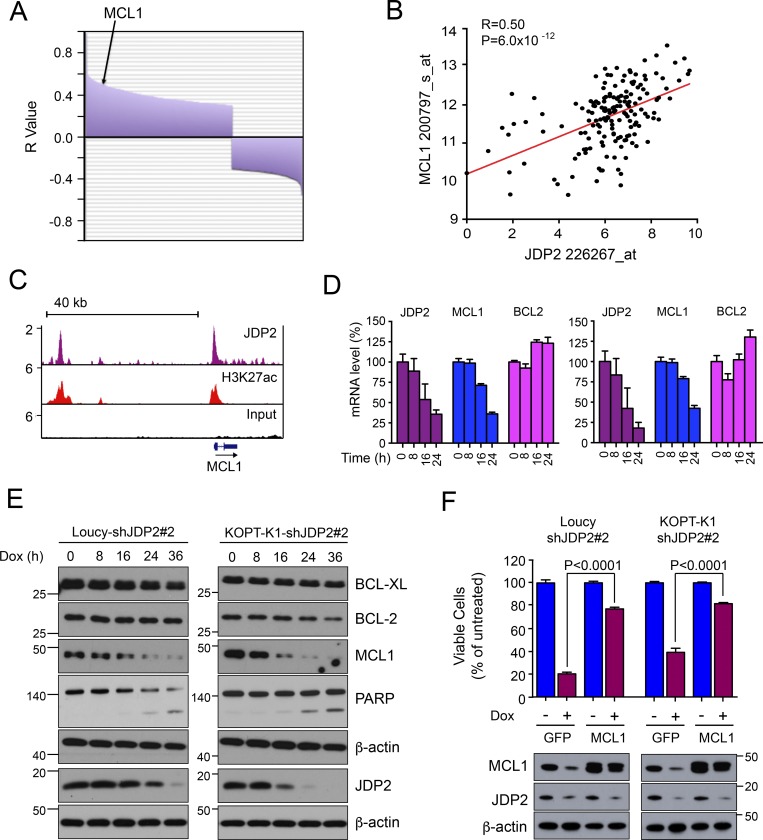
Figure 4.
JDP2 prevents apoptosis by directly regulating MCL1. (A) Waterfall plot showing genes most closely correlated with JDP2, using Pearson correlation analysis of gene expression data from 165 T-ALL patients from the MILE study (Haferlach et al., 2010). The y axis represents the Pearson correlation coefficient (R value) positively and negatively associated with JDP2 expression, adjusted for multiple testing using the false discovery rate, and P < 0.001. Genes are distributed across the x-axis, with position of MCL1 highlighted. (B) Direct correlation between JDP2 and MCL1, from Fig. 4 A, is shown in detail together with line of best fit. (C) ChIP-seq tracks for JDP2 and H3K27ac at the MCL1 locus in Loucy cells. (D) Relative JDP2, MCL1, and BCL2 mRNA levels over time after the addition of doxycycline to Loucy cells (left) and KOPT-K1 cells (right) stably expressing doxycycline-inducible JDP2 shRNA#2. qPCR experiments were performed in triplicate and verified in two independent experiments. (E) Western blots showing kinetics of MCL1 depletion and PARP1 cleavage after the addition of doxycycline in Loucy and KOPT-K1 cells expressing a doxycycline-inducible JDP2 shRNA. Representative Western blot from two separate experiments is shown. (F) Doxycycline-inducible JDP2 shRNA expressing Loucy and KOPT-K1 cells were stably transduced to express either GFP (control) or MCL1, and then treated with or without doxycycline, and viable cell number was measured by Cell Titer Glo at 24 h. Bottom: Western blots showing MCL1 and JDP2 expression in the transduced cell lines. P values were calculated using two-tailed Student’s t test applied to triplicate experiments performed twice. Data points represent the mean ± standard error of the mean.