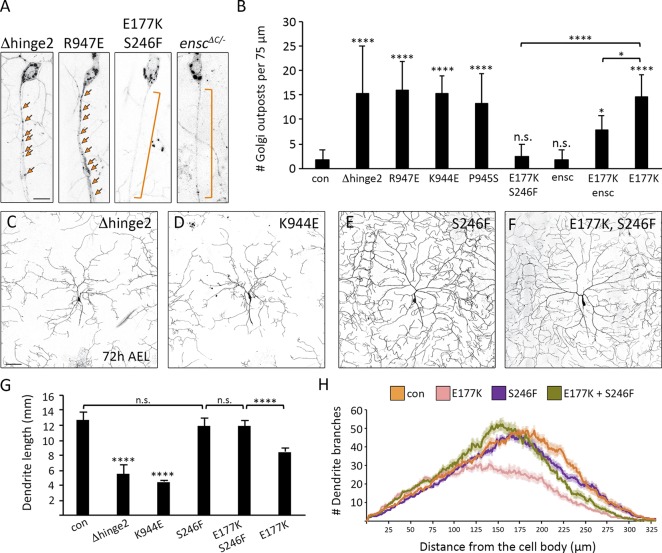
Figure 5.
Khc mutations that disrupt autoinhibition result in the axonal mislocalization of Golgi outposts and perturb dendrite arborization. (A and B) Representative images and quantification of Golgi outposts in control and mutant neurons. Mutations that disrupt autoinhibition (Δhinge2, K944E, R947E, and P945S) result in the axonal mislocalization of Golgi outposts. Effects of the E177K mutation are rescued by the S246F mutation and the loss of ensconsin (enscΔC/−). Bracket indicates axon, and arrows indicate outposts. Bar, 10 µm. Quantification of Golgi outposts (mean ± SD) in the proximal 75 µm of axons in 12 (KhcΔhinge2/−, KhcE177K/−),13 (KhcR947E/−, KhcP945S/−), 14 (KhcK944E/−, enscΔC/−), and 15 (control, KhcE177K,S246F/−, double-mutant KhcE177K/−, enscΔC/−) neurons from at least five larvae. (C–H) Representative images (C–F) and quantification (G and H) of dendrite arbors in control and mutant neurons at 72 h AEL. Bar, 50 µm. Mutations that disrupt autoinhibition (Δhinge2, K944E) result in smaller dendritic arbors (C, D, and G). The S246F mutation does not affect dendrite morphology (E, G, and H) and rescues arbor reduction caused by the E177K mutation (F–H). Quantification (G) of total dendrite length (mean ± SD) and Sholl analysis (H) of branch distribution (mean ± SEM) in 13 (KhcE177K,S246F/−, KhcE177K/−), 15 (KhcΔhinge2/−, KhcK944E/−, KhcS246F/−), and 16 (control) neurons from at least four larvae (G). The critical radius and maximum branches determined by Sholl analysis are reported in Table 2. *, P = 0.05–0.01; ****, P < 0.0001; and n.s. relative to control and evaluated by one-way ANOVA and Tukey post hoc test (G and H).