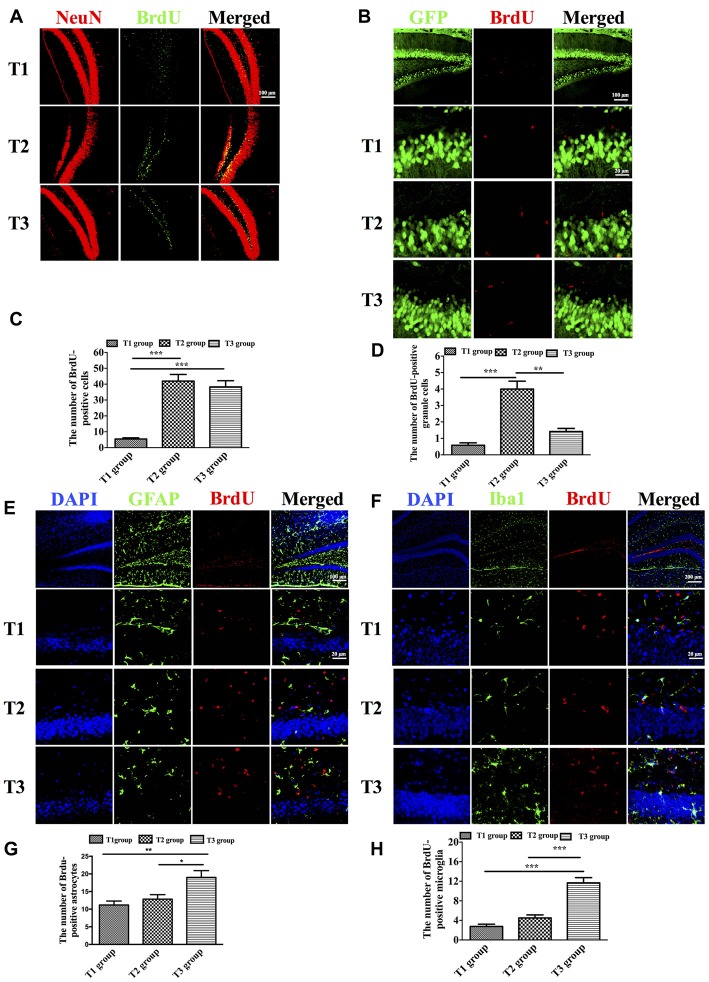
Figure 3.
Intermittent voluntary wheel running facilitated newborn cells to differentiate into granule cells in the dentate gyrus (DG) in middle-aged mice. (A) Representative images of newborn neurons in the DG labeled by anti-BrdU and anti-NeuN. Scale bar = 100 μm. (B) The number of BrdU-positive cells was significantly increased in the T2 and T3 groups compared with the T1 group. (C) Representative images of newborn granule cells, which were labeled by anti-BrdU and green fluorescent protein (GFP) in Thy1-GFP transgenic mice. Low magnification: scale bar = 100 μm; high magnification: scale bar = 20 μm. (D) The BrdU-positive granule cells were significantly increased in the T2 group compared with the T1 and T3 groups. (E) Representative images of newborn astrocytes labeled by anti-BrdU and anti-glial fibrillary acidic protein (anti-GFAP). Low magnification: scale bar = 100 μm; high magnification: scale bar = 20 μm. (F) The BrdU-positive astrocytes were significantly increased in the T3 group compared with the T1 and T2 groups. (G) Representative images of repopulated microglia labeled by anti-BrdU and anti-Iba1. Low magnification: scale bar = 200 μm; high magnification: scale bar = 20 μm. (H) The number of BrdU-positive microglia was significantly increased in the T3 group compared with the T1 and T2 groups. Data are presented as means ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001.