FIGURE 2.
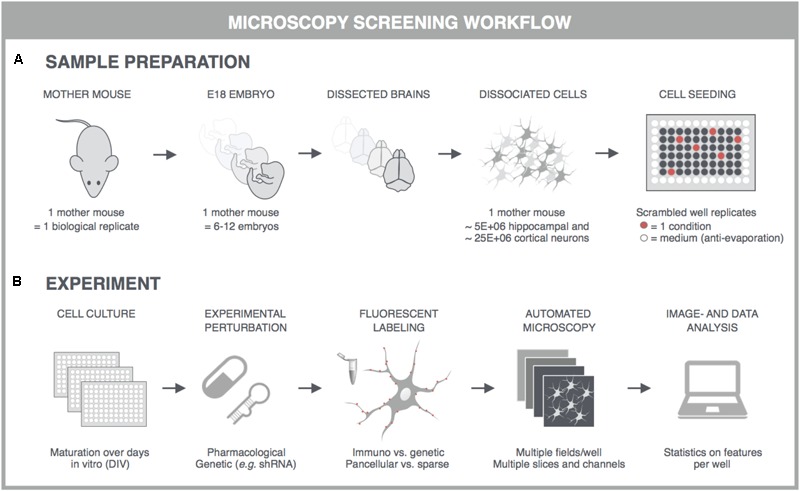
General principles for high-content screening with primary neuronal cultures. Although the sample preparation is more tedious and variable, primary cultures offer a level of synaptic connectivity that cannot be matched by immortal cell lines. The following steps are typically followed in synapse, spine or functional screens. (A) One dam is regarded as one biological replicate, and embryos, typically E17-18, of the same dam are pooled to obtain sufficiently large suspensions of cortical or hippocampal cells. Cells are seeded into multiwell plates of which the outer wells are filled with sterile medium, and the well replicates scrambled to avoid edge effects. (B) In high-content experiments, neuronal cultures are dosed and fluorescently labeled using an automated liquid handling system (genetic labeling is usually done before perturbation whereas immunostaining after). Images are captured on an automated microscope which is equipped to allow rapid acquisition, e.g., by employing multiple sensitive cameras with large fields-of-view for parallelization of fluorescence channels. Since primary neuronal cultures can show a heterogeneous distribution, multiple fields are captured per well. These fields are analyzed with high-content image analysis scripts and the resulting data is presented per well. Finally, statistics, data mining and visualization aid the interpretation, after which a secondary screen or low-throughput confirmation experiments can be conceived. This figure was adapted from Verstraelen et al. (2017) with permission.
