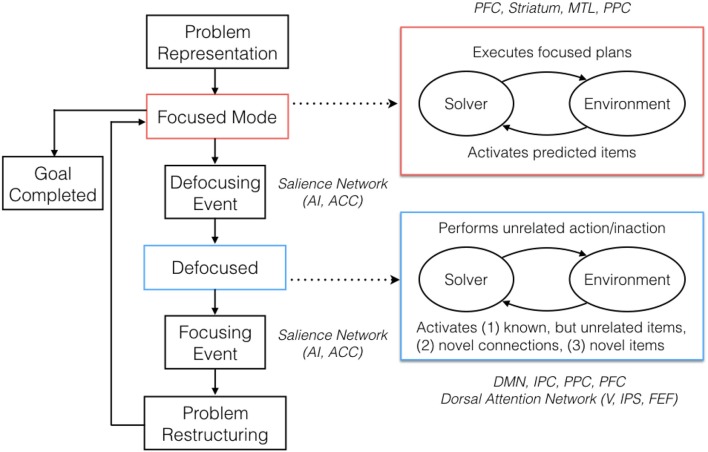
Figure 2.
Proposed Model for Real World Problem Solving (RWPS). The corresponding neural correlates are shown in italics. During problem-solving, an initial problem representation is formed based on prior knowledge and available perceptual information. The problem-solving then proceeds in a focused, goal-directed mode until the goal is achieved or a defocusing event (e.g., impasse or distraction) occurs. During focused mode operation, the solver interacts with the environment in directed manner, executing focused plans, and allowing for predicted items to be activated by the environment. When a defocusing event occurs, the problem-solving then switches into a defocused mode until a focusing event (e.g., discovery) occurs. In defocused mode, the solver performs actions unrelated to the problem (or is inactive) and is receptive to a set of environmental triggers that activate novel aspects using the three mechanisms discussed in this paper. When a focusing event occurs, the diffused problem elements cohere into a restructured representation and problem-solving returns into a focused mode.