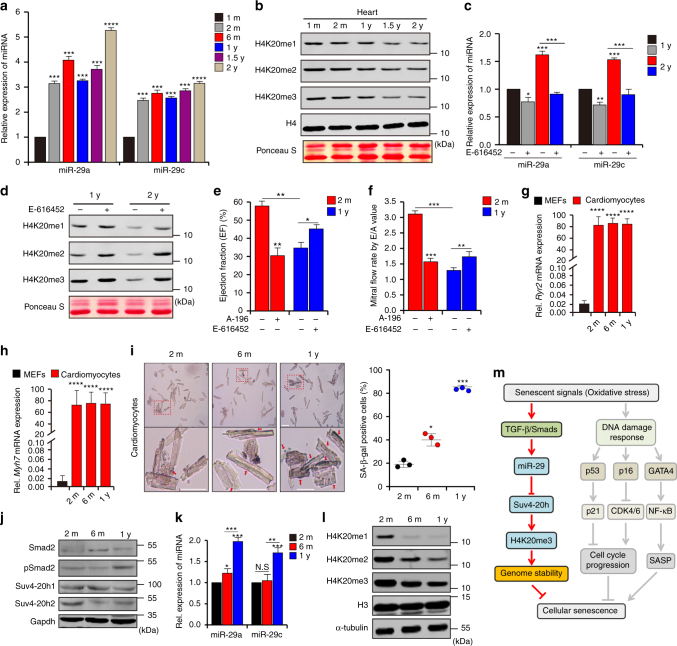
Fig. 6.
TGF-β/miR-29/H4K20me3 is involved in aging-associated cardiac dysfunction. a RT-qPCR to measure miR-29 expression, normalized to U6, in murine hearts (n = 4 per age) of the indicated ages (1-month-old, 1 m; 2-month-old, 2 m; 1-year-old, 1 y; 1.5-year-old, 1.5 y; 2-year-old, 2 y). b Western blot for H4K20 methylation in hearts of the indicated ages. c RT-qPCR to examine miR-29 expression in hearts of 1 y and 2 y mice, fed with DMSO or E-616452. The error bars represent the s.d obtained from triplicate independent experiments. d Western blot for H4K20 methylation in hearts from c. e, f Mice (2 m) fed with DMSO (n = 4) or A-196 (n = 4) and mice (1 y) treated with DMSO (n = 8) or E-616452 (n = 8) were subjected to cardiac function analysis using an echocardiographic imaging system (VisualSonics Vevo 2100, USA). EF (e) represents the ejection fraction of left ventricular flow, whereas E/A (f), the peak early filling (E-wave)/late diastolic filling (A-wave), represents the mitral flow rate. Representative images are shown in Supplementary Fig. 7e, f. The error bars represent the s.d. of the mean values. g, h RT-qPCR analysis of Ryr2 (g) and Myh7 (h) expression in cardiomyocytes isolated from mice of the indicated ages. i SA-β-gal staining of cardiomyocytes from mice as in g. The lower panel shows the magnified cells enclosed by red rectangular boxes in the images in the upper panel. Scale bar = 20 μm. The plot shows the proportion of SA-β-gal-stained cells among the different age groups. j Western blot for the indicated proteins in cells from i. k RT-qPCR for miR-29 expression in isolated cells from i. l Western blot for H4K20 methylations in cells from f. m Mechanisms proposed in this study. When cells undergo senescence-inducing stimuli, such as oxidative stress, TGF-β signaling is activated and serves as the signal transducer that promotes acute accumulation of miR-29, which in turn results in suppression of Suv4-20h and reduction in H4K20me3 abundance, leading to defective DNA damage repair and impaired maintenance of genome stability, and thus accelerating cellular senescence. Gapdh, H3 and α-tubulin were loading controls. Two-tailed unpaired Student’s t-tests, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001