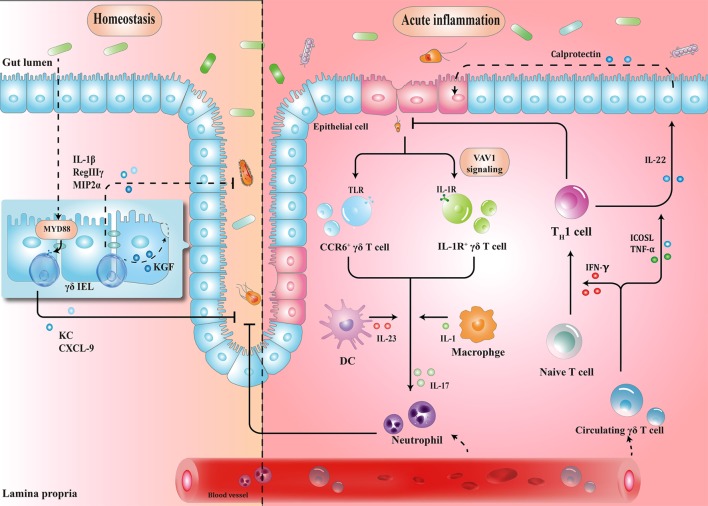
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the protective roles of γδ T cells in homeostasis maintenance and immune surveillance. (1) Physiologically, the crosstalk between microbiota, epithelial cells (ECs), and γδ T cells enhances barrier stabilization. (2) During acute inflammation, neutrophils are stimulated by IL-17 from γδ T cells, and recruited to eliminate pathogens. Meanwhile, microbe-activated circulating γδ T cells promote cytotoxic responses with Th1-committed αβ T cells and potentiate the release of calprotectin in an inducible T-cell co-stimulator ligand (ICOSL)/tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α)-dependent manner. IEL, intraepithelial lymphocyte; MYD88, myeloid differentiation primary response 88; KC, keratinocyte-derived chemokine; CXCL, chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand; MIP2α, macrophage inflammatory protein 2α; CCR, C-C motif chemokine receptor; TLR, toll-like receptor; IFN-γ, interferon γ; IL-17, interleukin-17.