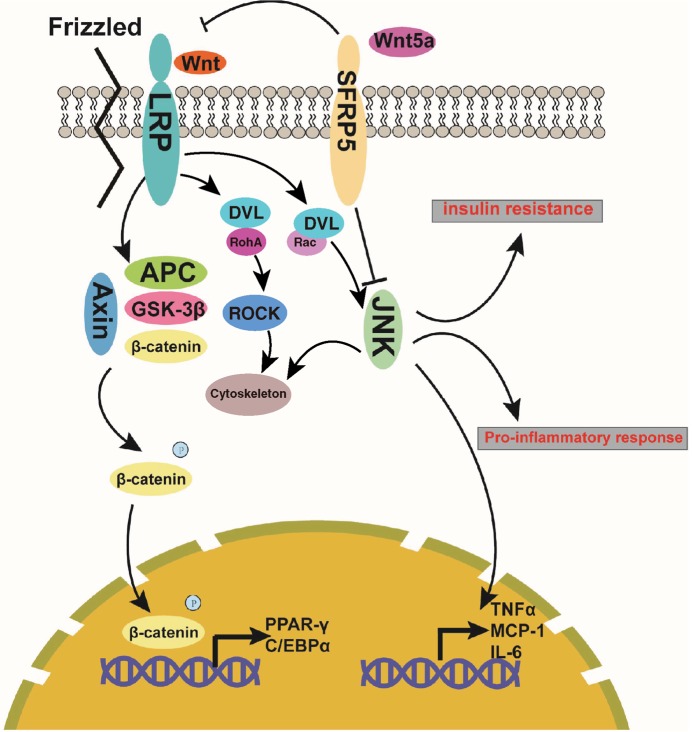
Figure 1. The mechanistic map of action of SFRP5 in adipogenesis through the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and signaling map in relation to the effect of SFRP5 on inflammation and insulin sensitivity.
Frizzled receptors can form complex with LRP in a manner of transmembrane protein and then the extracellular Wnt protein is combined with the complex, making the signal transmitted into cells. Following this, Axin/APC/GSK-3β complex is formed and combined with β-catenin, which leads to the activation of β-catenin through phosphorylation. Activation of β-catenin (transferring from cytoplasm to nucleus) thereby commits to the transcription of the target genes in the downstream, such as PPAR-γ and CEBPα. For the Wnt/PCP signaling pathway, Wnt binds to Frizzled receptors on the surface of cells and subsequently delivers signals into the cells to activate the downstream GTPase Rho and JNK, thus participating in the cytoskeleton and regulation of downstream genes of JNK signaling. SFRPS is capable of preventing the binding of Wnt and Frizzled proteins through its combination with Wnt protein, thus blockading the Wnt signaling, inhibiting the phosphorylation activation of β-catenin, and the transcription of the target genes (PPAR-γ and CEBPα) in the downstream. In addition, SFRPS has the ability to repress the JNK signaling via its combination with Wnt5a, leading to the suppression of TNF-α, MCP-1, and IL-6; as a result, the pro-inflammatory response and insulin resistance are reduced. Abbreviation: IL-6, interleukin-6.