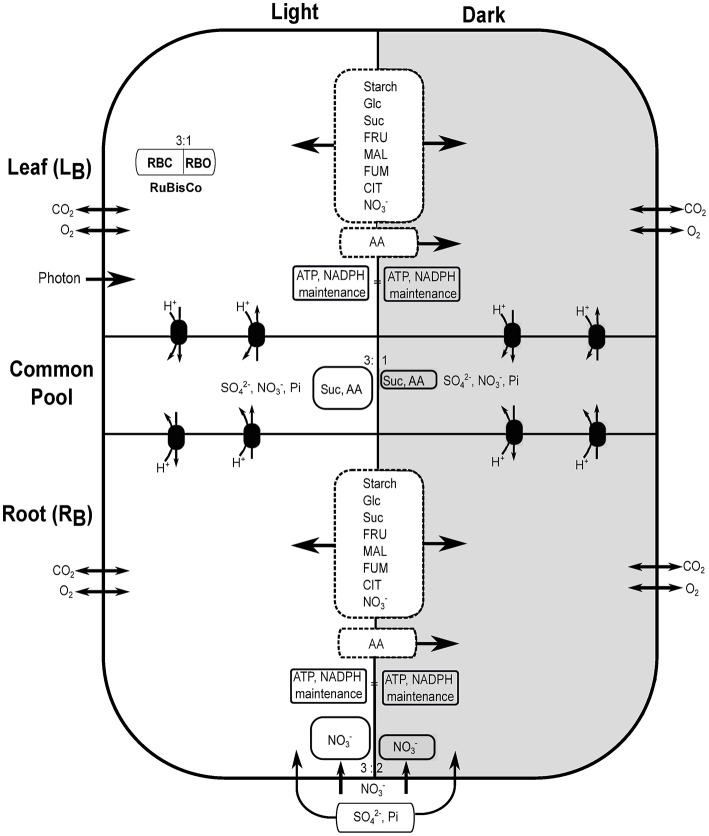
Figure 1.
Schematic description of diel leaf-root metabolic model of Arabidopsis thaliana. Light and dark phases are represented with white and dark backgrounds, respectively. The ratio of rubisco carboxylase (RBC):oxygenase (RBO) was set to 3:1 in all phases (only leaf in the light is shown). Starch, glucose (Glc), sucrose (Suc), fructose (FRU), malate (MAL), fumarate (FUM), citrate (CIT), and nitrate () were allowed to accumulate in the light and dark phases of leaf and root (dashed rectangle between light and dark where arrows indicate bidirectional storage). AA represents the 18 different amino acids. AA can be stored in the light and utilize in the dark. Exchange of AA, Suc, sulfate (), nitrate and phosphate (Pi) were allowed between leaf and root through the common pool using an active proton pump. Nitrate and photon uptake were allowed through root and leaf, respectively, at a maximum rate quantified by the corresponding tissue biomass. Uptake of other mineral nutrients (, Pi, etc.) were allowed only through the root. Gaseous exchange of CO2 and O2 were allowed in all four modules.