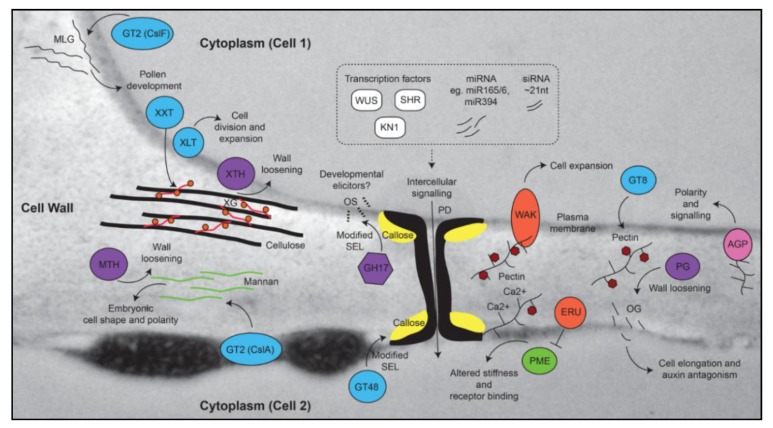
Figure 2.
Cell wall components that contribute to growth, development, and differentiation. The model shows polymers superimposed on a TEM image of a leaf cell wall, including 1,3;1,4-β-glucan (MLG), cellulose, xyloglucan (XG), mannan, callose, and pectin. Enzymes that contribute to the biosynthesis or modification of these components are shown. The spatial separation of polymers is only shown for schematic purposes. Biosynthetic enzymes are shown in blue, hydrolytic enzymes are shown in purple, receptors are shown in orange, mobile transcription factors are shown in white, pectin methylesterase (PME) is shown in green, and arabinogalactan protein (AGPs) in pink. Deposition and hydrolysis of callose at the neck of plasmodesmata (PD) can alter the size exclusion limit (SEL) of the PD, hence limiting the mobility of intercellular signaling molecules such as transcription factors (e.g., WUSCHEL [59], SHORT ROOT [60], and KNOTTED [61]), microRNAs (miRNAs [60,62]), and short interfering RNAs (siRNAs [63,64]). Hydrolysis of callose by GH17 enzymes leads to the release of stimulatory oligosaccharides (OS) from the glucan backbone in fungi, but it remains unclear if similar OS contribute to growth and development in plants. By contrast, release of oligogalacturonides (OG) from pectin by polygalacturonase (PG) has been implicated in plant development through antagonistic effects on auxin pathways. The small circles on XG indicate galactosyl residues present due to the activity of XLT2 (xyloglucan galactosyltransferase). GT8 family enzymes contribute to the biosynthesis of pectin, which is usually synthesized in a methylesterified form (e.g., methylesterified homogalacturonan; meHG). Removal of methylesters (red hexagons) through the activity of PME can lead to calcium binding and subsequent cross-linking of pectin polysaccharides, which influences wall stiffness. GT, glycosyltransferase, XXT, xylosyltransferase, MTH, mannan transglycosylase/hydrolase, XTH, xyloglucan transglycosylase/hydrolase, CslF, cellulose synthase-like F, CslA, cellulose synthase-like A, GH, glycosyl hydrolase, WAK, wall-associated kinase, ERU, ERULUS receptor-like kinase.