Figure 6.
Conformational Changes during Isomerization and a Proposed “Coupled Load and Unwind” Initiation Model
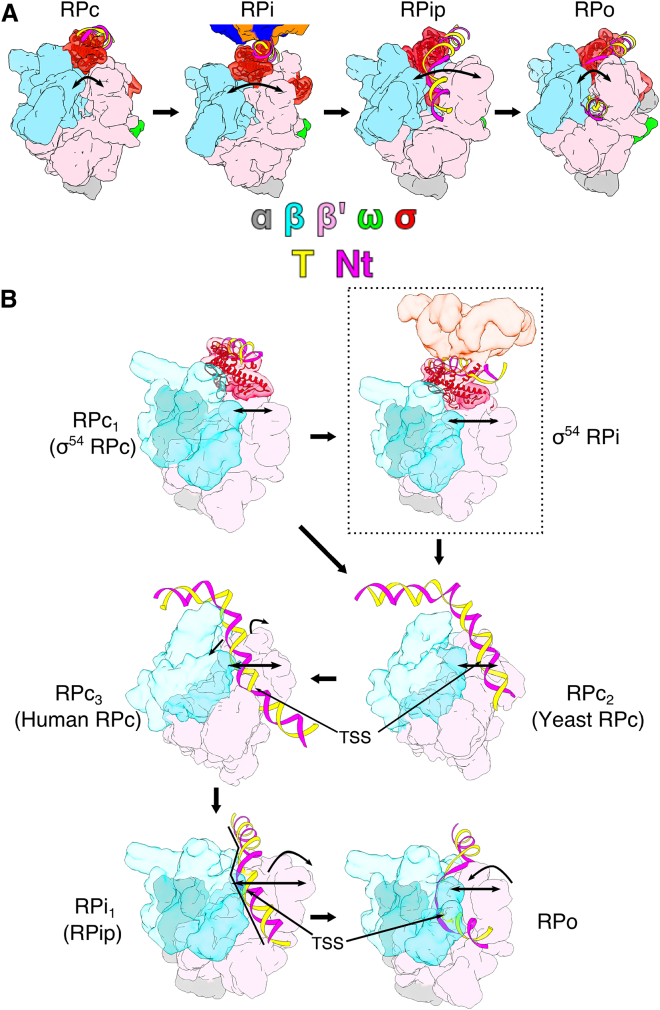
(A) Conformational changes from RPc to RPo in σ54 system. RNAP cleft opens initially from RPc to RPi to RPip before closes down in RPo. These are correlated with DNA path and σ54 conformations. RNAP in surface representation, σ54 and DNA in ribbon cartoon. Arrows indicate clamp opening.
(B) Proposed transcription initiation model. The initial closed complex is system specific; shown here is σ54 RPc (PDB: 5NSR, labeled RPc1) where DNA is high above the RNAP cleft. RNAP is then converted to RPi in σ54 system but could go to a conformation similar to those captured in yeast Pol II closed complex (RPc2, PDB: 5FZ5), before transition to RPc2 as captured in human Pol II closed complex (PDB: 5IYA) where the RNAP clamp is slightly open and DNA starts to bend into the RNAP cleft. In RPi1 (RPip), DNA makes a 30° kink in σ54 (>60° in σ70) and is at the entrance to the RNAP cleft with the clamp wide open. Clamp closure to RPo causes the DNA to load and unwind.
See also Figure S7.