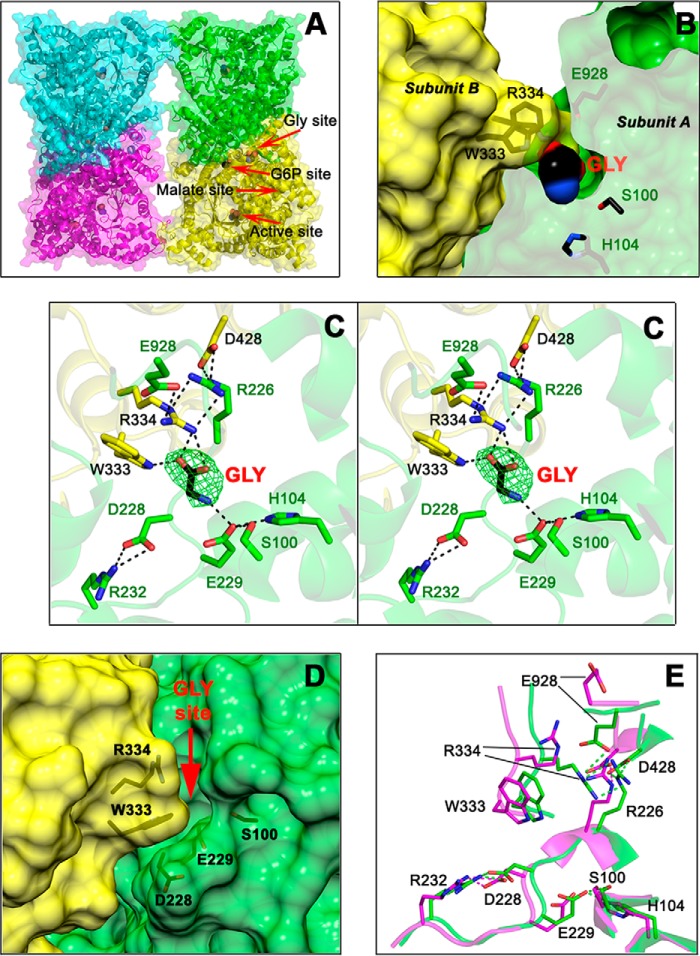
Figure 2.
The allosteric-site for neutral amino acids of ZmPEPC-C4. A, cartoon and surface representations of the fold and secondary structure elements of the tetrameric ZmPEPC-C4 in complex with glycine. Red arrows indicate the position of the allosteric site for neutral amino acids with a glycine bound, of the active site with an acetate bound, of the putative allosteric site for G6P also with an acetate bound, and of the empty allosteric site for l-malate. B, transverse section of a dimeric unit showing the glycine molecule bound inside its allosteric site. Residues are colored green or yellow depending on the monomer. C, stereoview showing the residues and interactions of the allosteric site for neutral amino acids. The simulated annealing omit map (Fo − Fc) of the bound glycine molecule is shown contoured at 3.0 σ level (green mesh). D, surface representation of the monomer–monomer interface showing the crevice of the neutral amino acid allosteric site as seen in the previously reported 1JQO ZmPEPC-C4 crystal structure where this site is empty and open. The red arrow marks the position of the glycine activator in the 5VYJ ZmPEPC-C4 crystal structure reported here. E, differences in the conformation of critical residues of the allosteric site for amino acids between the 5VYJ ZmPEPC-C4 in complex with glycine (green carbon atoms) and the 1JQO ZmPEPC-C4 structure (magenta carbon atoms). Hydrogen bonds are depicted as black dashed lines (C) or green and magenta (E); cutoff is 3.0 Å. In B, C, and E, the side chains of relevant protein residues are shown as sticks with oxygen atoms in red, nitrogen in blue, and carbons in green, yellow, or magenta. Glycine and acetate molecules are depicted as spheres colored similarly but with black carbons. A, C, and E were generated using PyMOL. B and D were generated using the UCSF Chimera package (52).