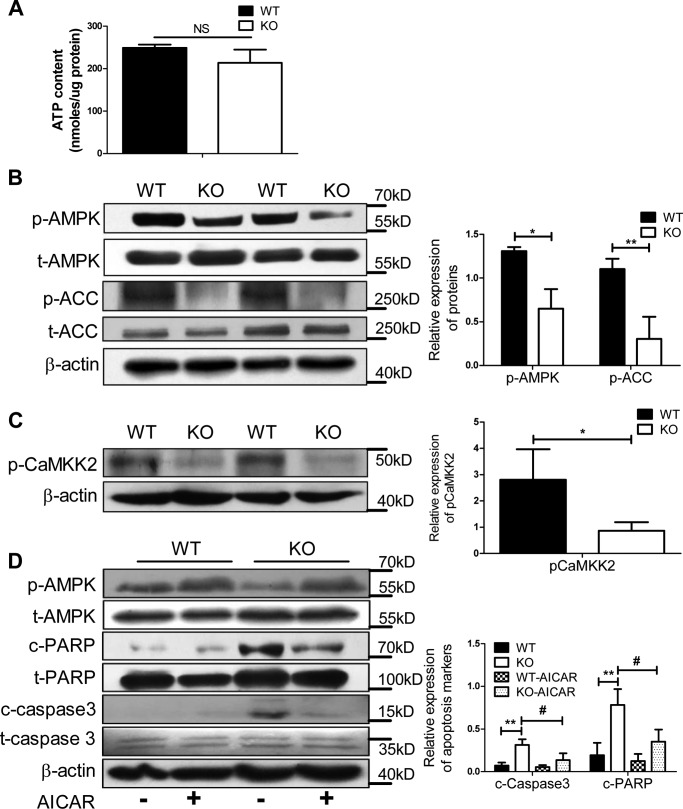
Figure 3.
Loss of Ei24 impairs AMPK activation and induces apoptotic cell death. A, ATP content of islets (40 islets/group), which were cultured in RPMI medium 1640 with 10% FBS from WT and KO mice at 8 weeks of age. Data were normalized to protein content. Data were obtained from three independent experiments. B, Western blotting for p-AMPK, t-AMPK, p-ACC, and t-ACC in the isolated islets (150 islets/group) from WT and KO mice at 8–10 weeks of age. C, Western blotting for p-CAMKK2 in the isolated islets (150 islets/group) from WT and KO mice at 8–10 weeks of age. D, Western blotting for p-AMPK, t-AMPK, c-PARP, t-PARP, c-caspase-3, and t-caspase-3 in the isolated islets (150 islets/group) with or without AICAR treatment from WT and KO mice at 8–10 weeks of age. β-Actin served as the loading control. Data were obtained from three independent experiments. Data are expressed as the mean ± S.D. (error bars): WT versus KO (*, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01) and KO group without AICAR treatment versus KO with AICAR treatment (#, p < 0.05).