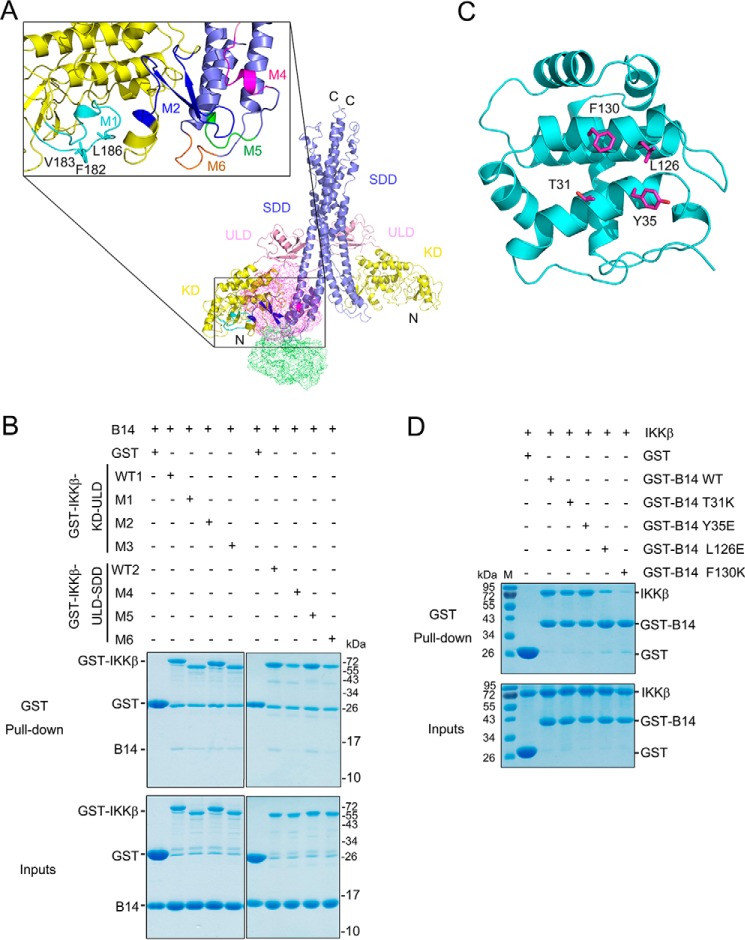
Figure 3.
The M2 and M4 segments of IKKβ are required for B14 binding. A, molecular docking models of IKKβ–B14 interaction. The KD, ULD, and SDD of human IKKβ (PDB ID 4E3C) are colored yellow, pink, and slate, respectively. The potential B14-interacting segments present on IKKβ protein are shown as M1, M2, and M4-M6 and colored cyan, blue, magenta, green, and orange, respectively. Three residues, Phe-182, Val-183, and Leu-186 on the M3 segment, are shown in stick representation and colored cyan. B, pulldown of B14 by GST-IKKβ mutants. GST protein alone was used as a negative control. GST-IKKβ-KD-ULD contains residues 1–384 of human IKKβ, and GST-IKKβ-ULD-SDD harbors residues 307–678 of human IKKβ, both of which are used as the WT positive controls (WT1 and WT2). In addition, the M1 mutant has residues 179–197substituted with GGGGSGGS, M2 has residues 235–260 replaced with GGGGSGGS, M3 contains F182K/V183K/L186K mutations, M4 has residues 408–416 replaced with GGGGS, M5 has residues 421–426 substituted with GGGGS, and M6 has residues 577–583 replaced with GGGGS. C, the B14 structure is represented as a ribbon diagram and is colored cyan, with the potential IKKβ interacting residues shown as stick representation and colored magenta. D, pulldown of human IKKβ (1–675, S177E/S181E) by GST-B14 mutants. All experiments were repeated three times and yielded similar results. M stands for protein molecular weight standard marker.