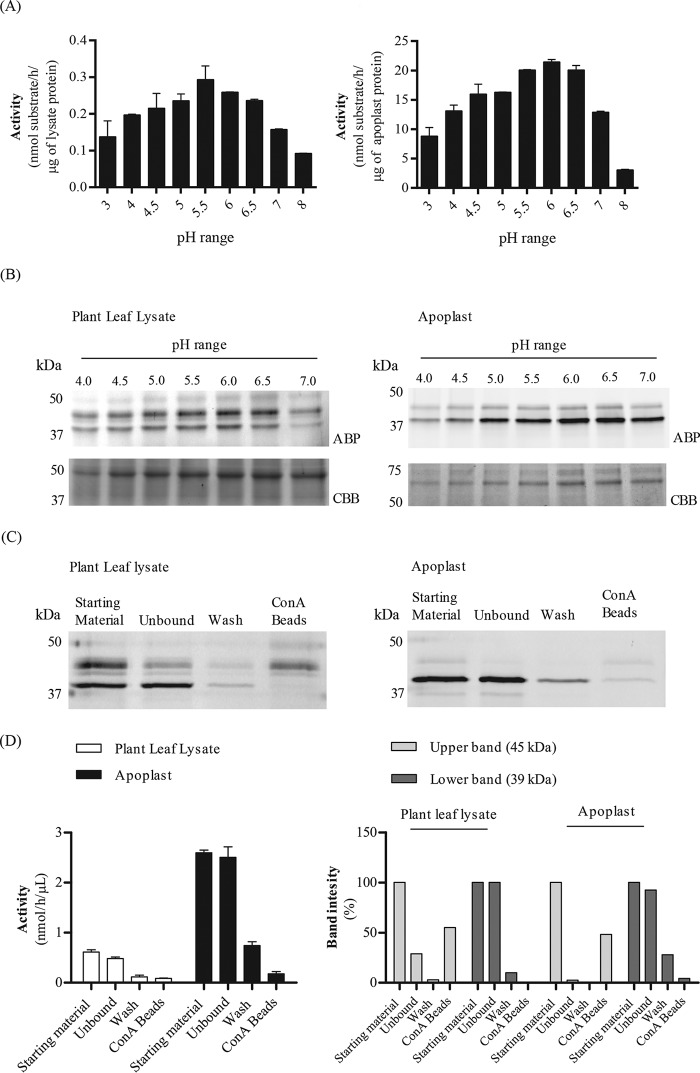
Figure 1.
Screening for α-galactosidases in N. benthamiana. Plant leaf lysates and apoplast samples were tested on their α-galactosidase activity via 4MU–Gal assays and ABP in vitro labeling, following in-gel detection of the labeled proteins. A, 4MU–α-Gal activities present in plant leaf lysates and apoplast samples were first examined at different pH values of 3–8. (n = 2, error bars indicate mean ± S.D.) B, 45 μg of plant leaf lysate and 12 μg of apoplast sample were incubated with 0.25 μm TB474 for 30 min at pH 4–7 at room temperature. Labeled proteins were detected via in-gel fluorescent scanning (ABP), and the gels were stained with Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) to show equal total protein loading. C, plant leaf lysates and apoplast samples were incubated with ConA-Sepharose beads for 2 h at 4 °C. After incubation, the samples were centrifuged, and different fractions were tested for α-galactosidase activity via ABP labeling and (D, left panel) 4MU–α-Gal assays. (n = 2, error bars indicate mean ± S.D.) In addition, D, right panel, quantification of the band intensity of C is presented. Samples tested: starting material = sample prior to ConA-Sepharose bead incubation, containing all proteins. Unbound = supernatant after incubation with the beads and centrifugation. This sample contains all material not bound to the beads. Wash = wash of the beads. Beads = pellet after incubation with the beads and centrifugation, containing the proteins attached to the ConA-Sepharose beads.