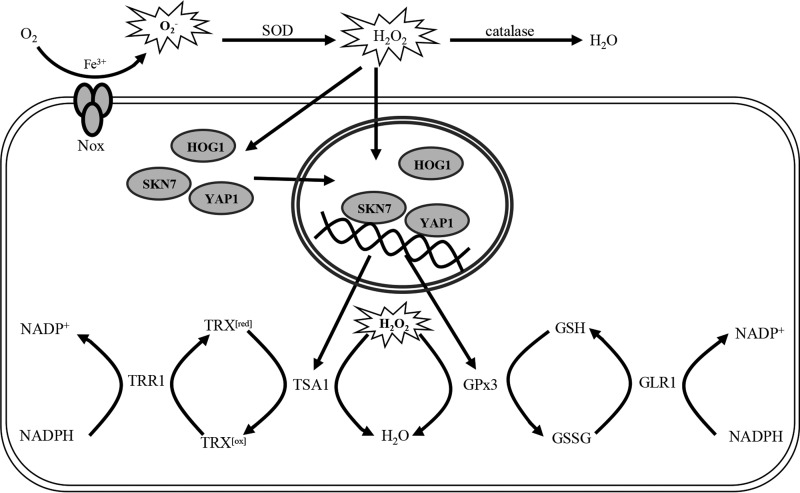
FIG 10.
Proposed network of transcriptional regulation that involves YAP1, SKN7, HOG1, NOX, GPx3, GLR1, TSA1, and TRR1 and leads to ROS detoxification in A. alternata. Low-level H2O2, generated by superoxide dismutases (SOD) from superoxide (O2−) produced by NOX, may serve as a signal that upregulates the expression of YAP1, SKN7, and HOG1, and nuclear localization of these proteins transcriptionally upregulates TSA1, TRR1, GPx3, and GLR1. TSA1 can detoxify H2O2 in conjunction with thioredoxin reductase (TRR1) and thioredoxin cycling between reduced thioredoxin (TRX[red]) and oxidized thioredoxin (TRX[ox]). GPx3 can detoxify H2O2 in conjunction with glutathione reductase (GLR1) and glutathione cycling between reduced glutathione (GSH) and oxidized glutathione (GSSG).