FIG 2.
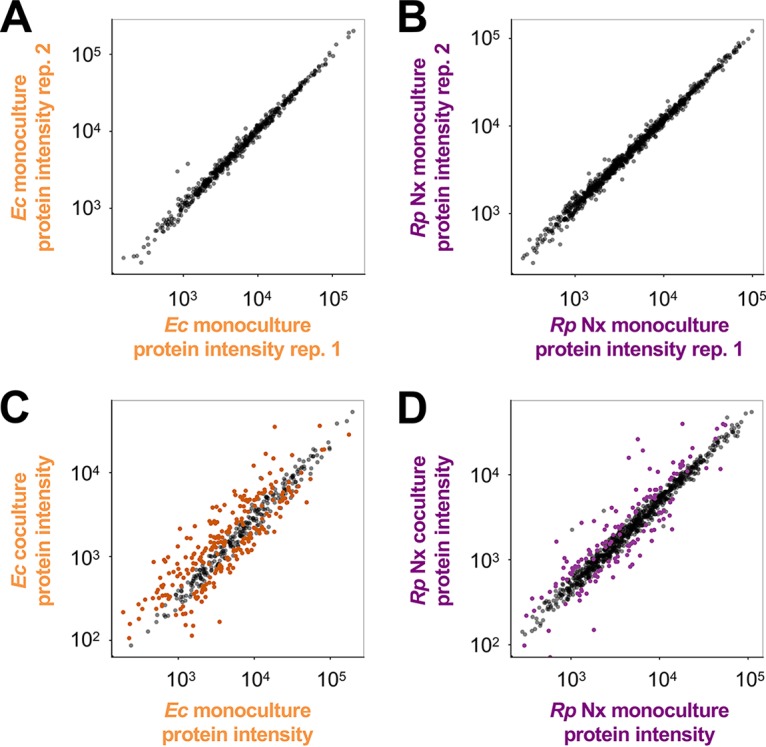
Coculture conditions result in altered protein expression patterns in both species, with more differences in WT E. coli than in R. palustris Nx. Protein expression (estimated by the LC-MS/MS sum of peptide intensities) of WT E. coli (left) (A and C) and R. palustris Nx (right) (B and D) comparing protein expression patterns between monoculture biological replicates (replicate 1 versus replicate 2) (A and B) and monoculture (average of data from monoculture replicates) versus coculture (C and D). Colored spots indicate significant differences in protein expression levels determined by using the median of normalized peptide ratios rather than summed peptide ratios. Significant changes in protein expression levels under coculture conditions at a false discovery rate of 1% were computed by determining the ratio, r, at which 99% of genes have a ratio less than r when comparing biological-replicate monocultures. Total protein sums are shown. Thus, gray spots that appear far from the center diagonal reflect proteins that did not show a significant change compared using the median of normalized peptide ratios.
