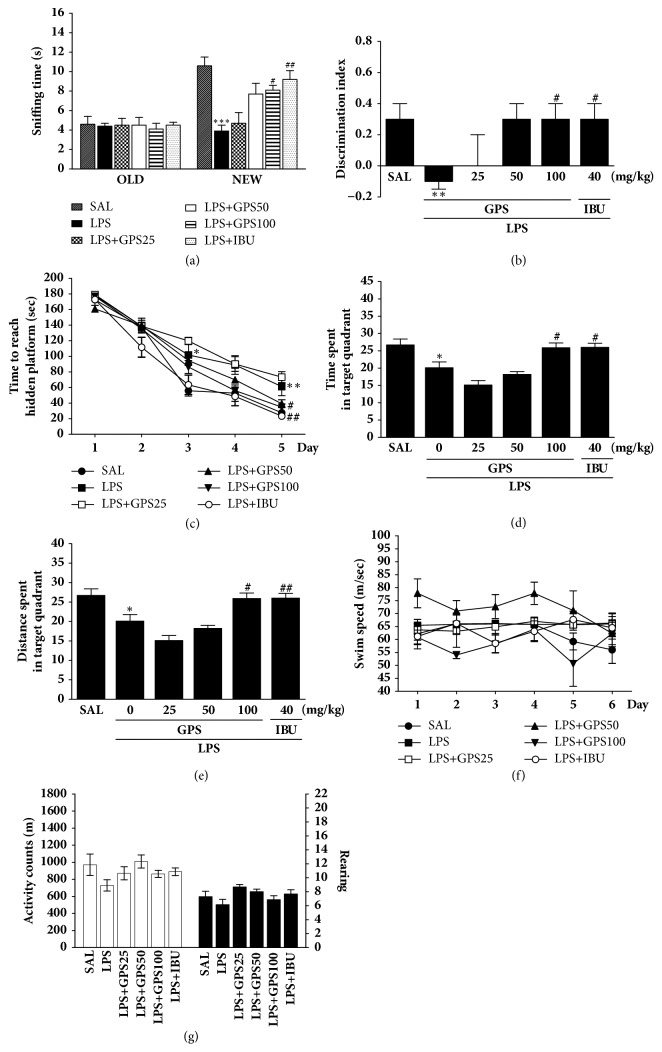
Figure 3.
Effects of GPS on recognition memory were evaluated using a novel ORT in which we analyzed the times taken to sniff familiar and novel objects during a 5-min choice trial (A) and the ability to discriminate between familiar and novel objects (B). The MWM test was used to evaluate the effect of GPS on spatial learning and memory; we analyzed the time taken to escape from water (latency) during acquisition trials using a submerged platform (C), the percentages of time spent in the target quadrant (D), the proportion of the total distance traversed in the target quadrant (E), and swimming speed (F). The OFT was used to evaluate the effect of GPS on locomotor activity and total number of rearings (G). ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 versus SAL group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.05 versus LPS group.