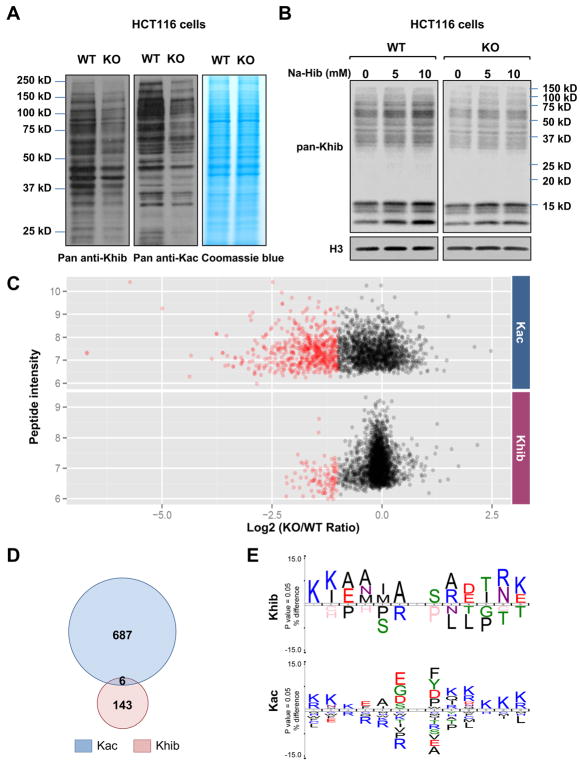
Figure 2. Deletion of p300 alters Khib levels on various protein substrates.
A) Deletion of p300 reduces Kac and Khib levels on various non-histone proteins. Total cell lysate from WT and p300 KO HCT116 cells were analyzed for Khib and Kac levels by immuno-blotting with indicated pan anti-Khib or anti-Kac antibody.
(B) 2-hydroxyisobutyrate dose-dependently increases total Khib levels on various cellular proteins in part through p300. WT and p300 KO HCT116 cells were treated with 2-hydroxyisobutyrate (Na-Hib) at indicated concentrations for 24 hours. Please note that Na-Hib treatment dose-dependently increased the Khib levels in WT cells, but this trend was blunted in p300 KO cells.
(C) p300 deficiency leads to systemic reduction of Khib and Kac on a number of protein substrates. The scatter plots show the ratio of Khib and Kac peptides in p300 KO vs WT cells in relation to average peptide intensities.
(D) p300 catalyzes Khib and Kac on distinct lysine residues in a variety of protein substrates. The Venn diagrams show overlap between p300-targeted Khib and Kac sites.
(E) The consensus sequence logos show enrichment of amino acid residues among the p300-targeted Khib and Kac sites.