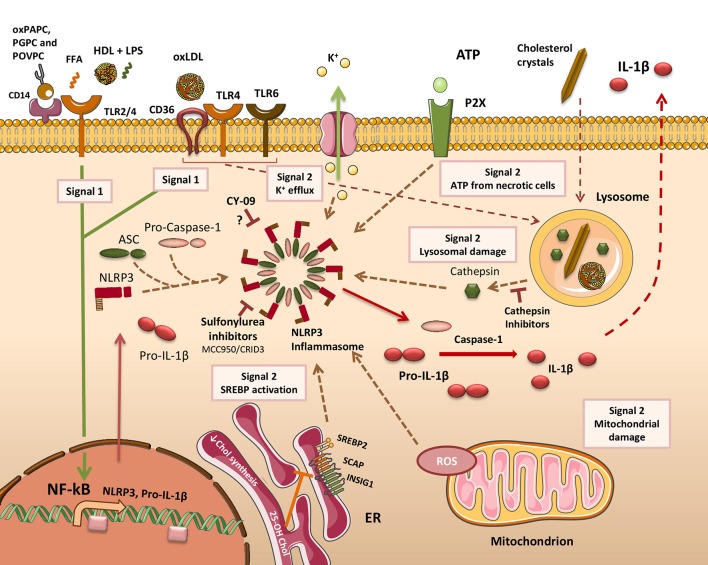
Figure 2.
Mechanisms of inflammasome activation in atherosclerosis. To facilitate the release of IL-1β (& IL-18) in macrophages (MO), two distinct signals must be delivered. Firstly, cells need to be primed (Signal 1) to activate the NF-κB-responsive genes NLRP3 and IL-1β. In atherosclerosis, a broad range of lipid and lipoprotein agonists provides this signal by activating cell surface pattern recognition receptors (PRRs). 1-palmitoyl-2-arachidonoyl-sn-3-glycero-phosphorylcholine (oxPAPC), 1-palmitoyl-2-glutaroyl-sn-glycero-phosphatidylcholine (PGPC), and 1-palmitoyl-2-(5-oxovaleroyl)-sn-glycero-phosphatidylcholine (POVPC) prime cells through CD14. Toll-like receptor 2 (TLR2) has also been described as an oxPAPC receptor. Free fatty acids (FFA) prime MOs through a TLR2-TLR4 signaling complex. The ApoAI moiety in High-density lipoprotein (HDL) can co-activate peritoneal MOs along with Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) through TLR2 or TLR4. Oxidized LDL (oxLDL) can prime MOs via signaling through a CD36-TLR4-TLR6 receptor complex. CD36 can additionally promote oxLDL uptake and its conversion into cholesterol crystals within phagolysosomes. The second signal (Signal 2) is required for assembly of the canonical NACHT, LRR and PYD domains-containing protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome complex. A number of different activating stimuli are able to deliver this signal. These include increased sterol-regulatory element-binding protein 2 (SREBP2) activity, mitochondria-derived reactive oxygen species (ROS), lysosome damage leading to cathepsin release, and exogenously-derived ATP from adjacent necrotic cells. Activation of surface P2X receptors leads to K+ efflux through ion channels. Inflammasome activation produces mature caspase-1 which cleaves pro-IL-1β (or pro-IL-18), forming mature bioactive IL-1β that is released from the cell. Cathepsin inhibitors diminish IL-1β release by inhibiting NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Other chemicals shown to inhibit the NLRP3 inflammasome include MCC950, which also reduces atherosclerosis in mice, and CY-09 that works through an unknown mechanism. SCAP, SREBP cleavage-activating protein; INSIG, insulin-induced gene protein.