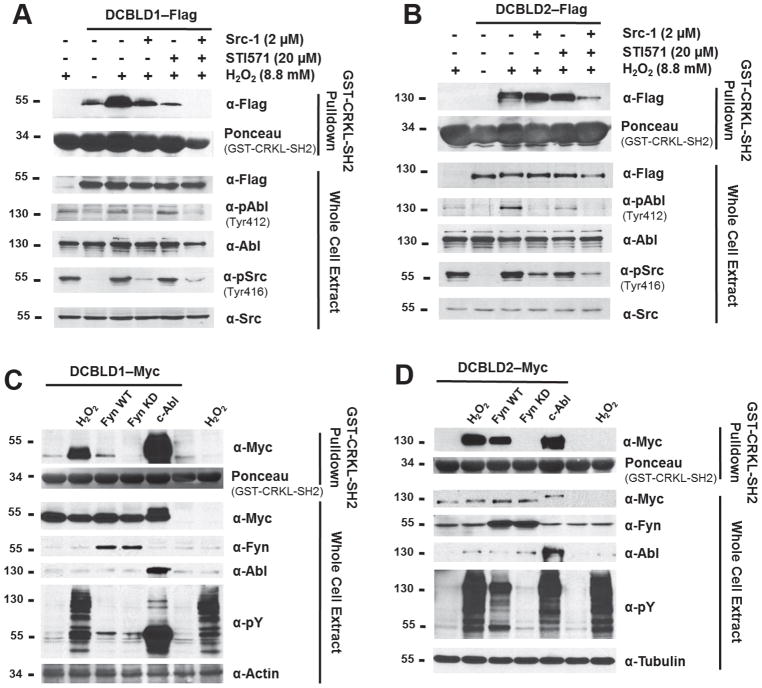
Figure 3.
SFKs and Abl are necessary and sufficient to induce DCBLD1 and DCBLD2 to bind to the CRKL-SH2 domain. Pulldown assays were performed from extracts of DCBLD1- and DCBLD2-transfected cells as described in the legend to Figure 2 above. (A) DCBLD1 binding was reduced upon treatment with the SFK inhibitor (Src-1). However, the Abl-specific inhibitor (STI571) more strongly disrupted the interaction. The application of both inhibitors abolished the interaction. (B) No significant reduction in the binding between DCBLD2 and the CRKL-SH2 domain was observed in response to either inhibitor alone. However, the application of both inhibitors strongly reduced the DCBLD2-CRKL-SH2 interaction. To determine whether these kinases were sufficient to induce this interaction, Fyn and c-Abl were co-transfected with (C) DCBLD1 or (D) DCBLD2. While Fyn was able to induce a small degree of binding between the CRKL-SH2 domain and DCBLD1, Abl was superior in this regard.