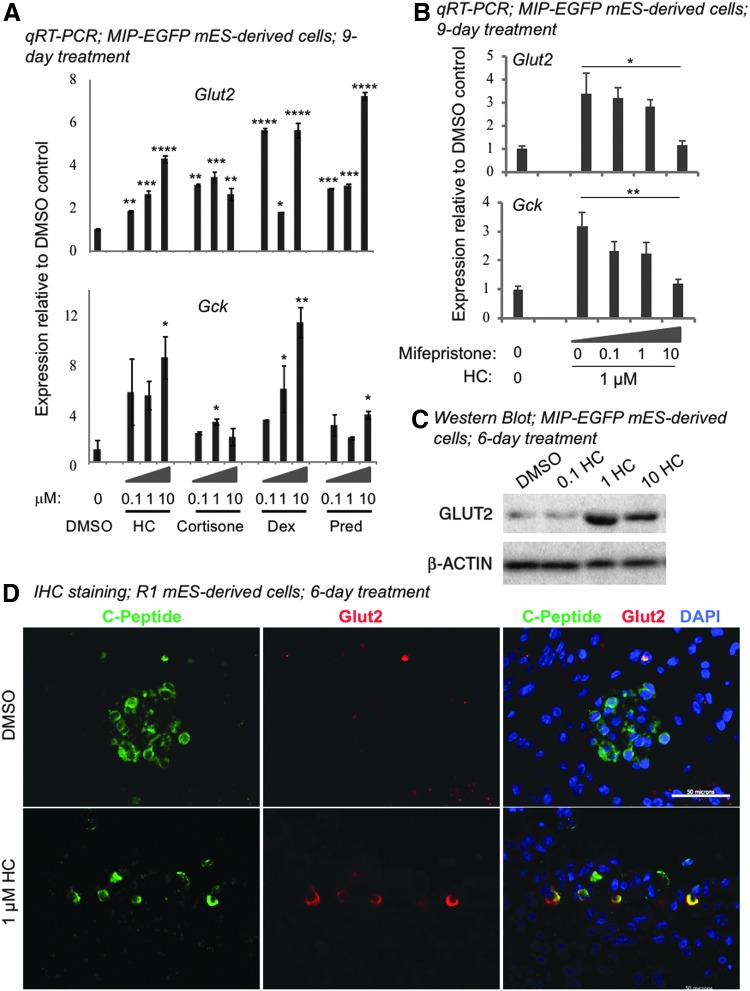
FIG. 3.
Glucocorticoids enhance expression of Glut2 and Gck in mES cell-derived beta-like cells through GR signaling. Day-18 cells derived from mES cells were cultured in the presence of designated glucocorticoids for 9 (A, B) or 6 (C, D) days. (A) qRT-PCR analyses showed that glucocorticoids enhanced the expression of Glut2 and Gck in MIP-EGFP mES-derived cells. β-Actin was used as the internal control. Data represent fold change compared to the DMSO vehicle control (designated as “0”). Data represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA. *, **, ***, and **** indicate P < 0.05, P < 0.01, P < 0.001, and P < 0.0001, respectively, compared to the DMSO control. (B) Mifepristone, a GR antagonist, inhibited the effects of HC on the expression of Glut2 and Gck. Data represent mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Significance was determined by one-way ANOVA. * and ** indicate P < 0.05 and P < 0.01, respectively. (C) Western blot analysis showed that protein expression of Glut2 was enhanced by HC. β-ACTIN was the loading control. (D) Double immunofluorescence staining showed that C-PEPTIDE expressing cells coexpressed GLUT2 after HC treatment of R1 mES-derived cells. Scale bar = 50 μm. HC, hydrocortisone; Dex, dexamethasone; Pred, prednisolone.