Fig 1.
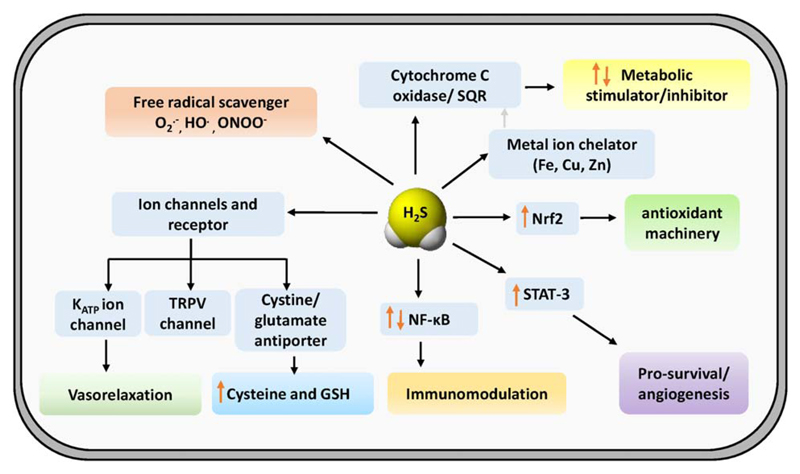
Molecular targets of H2S in mammalian system. Top left: H2S has the ability to directly scavenge reactive oxygen and nitrogen species (ROS/RNS). Top right: H2S targets metal cofactor of cytochrome c oxidase and leads to inhibition of cellular respiration. Oxidation of H2S by sulfide quinone oxidoreductase (SQR) couples catabolism of H2S with mitochondrial electron transport chain (ETC) and thus modulates cellular metabolism. Bottom left: ion channels which are involved in systemic responses to H2S in blood vessels, heart, and neurons. Bottom right: H2S targets cysteine thiols by S-persulfidation of intracellular signaling proteins and transcription factors which likely accounts for the downstream effects on inflammation, antioxidant response, cellular proliferation, and survival.