Table 1.
Summary of Common EDCs and their Histories, Uses, Sources and Effects*
| EDC | General chemical structure |
Group | Introduction date |
Restrictions | Route of exposure |
Sources | Half-life | Effects/animal model notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atrazine |
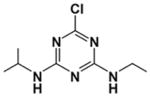
|
Chlorotriazine herbicide | 1959 | European Union ban 2004 | Ingestion, inhalation | Pesticide/herbicide, water and soil contaminant | 10–12 hours | Endocrine, respiratory and nervous system targets, liver damage |
| BPA |
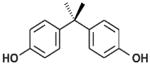
|
Bisphenols | 1960s | Varies by country. In the United States, voluntarily restricted in baby products 2012 | Ingestion, inhalation, dermal absorption | Polycarbonate plastics, epoxy resins, plastic toys and bottles, lining of food cans | 4–5 hours | Estrogenic, obesogenic, neurological effects, reproductive and developmental effects |
| DDT |
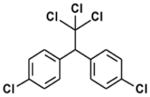
|
Organochloride | 1940s | Widely banned 1972 but still used in some countries. | Ingestion, inhalation, dermal absorption | Contaminated water, soil crops, fish | 6–10 years | Estrogenic, anti-androgenic, reproductive effects, carcinogen, central nervous system, kidney, liver and peripheral nervous system effects |
| DES |
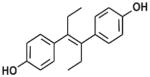
|
Non-steroidal synthetic estrogen | 1941–1947 | Restricted 1971–1975 | Ingestion, injection, vaginal suppository | Pharmaceutical for humans and livestock | 2–3 days | Transplacental carcinogen, teratogen |
| PCBs |
|
Organochloride | 1927 | Banned 1979 | Ingestion, inhalation, dermal absorption | Contaminated air and food, skin contact with old electrical equipment | 12 days to 16 years | Carcinogen, stomach and liver damage, reproductive and nervous system effects including IQ loss, thyroid injury |
| Phthalates |
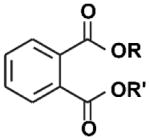
|
Plasticizers | 1920s | Restricted 2009 | Ingestion, inhalation, dermal absorption | Contaminated food, PVC plastics and flooring, personal care products, fragrance, medical devices and tubing | ~12 hours | Antiandrogenic activity, carcinogen, liver damage, reproductive and developmental effects, asthma, obesogen, possible neuroendocrine disruptor; Rat testis is vulnerable, mouse and human fetal testis xenografts are not. |
| PFOA |
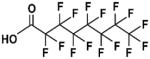
|
Fluorosurfactant | 1940s | United States 2015 voluntary production restriction | Ingestion, inhalation | Contaminated food and water, dust, floor waxes, fire fighting foam, electrical wiring, lining of food wrappers, stain resistant carpeting | 2–4 years | Liver, developmental, and immune system toxicant, carcinogen; Rats an inappropriate model |
| TCDD |
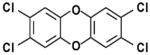
|
Polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin | Synthesized 1872 | Ingestion, inhalation | By-product of chlorinated herbicide production, smelting, chlorine bleaching of paper; can be naturally occurring | 7–11 years | Liver damage, weight loss, atrophy of thymus gland, immunosuppression, reproductive effects and cancer; susceptibility varies widely across species and strains | |
| Vinclozolin |
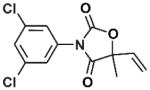
|
Dicarboximide fungicide | 1981 | Ingestion, inhalation, dermal absorption | Diet and occupational | Aerobic soil 28 days, plasma 20 hours | Antiandrogenic activity, male reproductive and neurological effects, transgenerational reproductive effects, potential carcinogen |
BPA=bisphenol A; DDT=dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane; DES=diethylstilbestrol; MXC=methoxychlor; PCBs=polychlorinated biphenyls; PFOA=perfluorooctanoic acid; TCDD= 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzodioxin
Adapted from Gore, A. C. et al. EDC-2: The Endocrine Society's Second Scientific Statement on Endocrine-Disrupting Chemicals. Endocr. Rev. 36, E1-E150, doi:10.1210/er.2015-1010 (2015).
