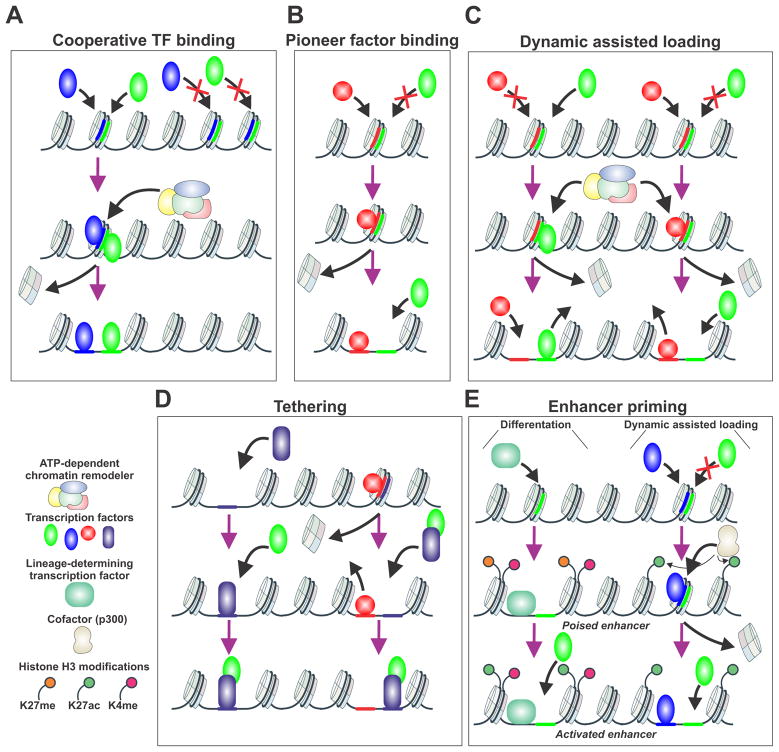
Figure 2.
Illustration of enhancer reprogramming models. (A) Cooperative TF binding model. The binding region of interest is inaccessible until two TF concomitantly binding, recruit chromatin remodeling factors resulting in an accessible region. (B) Pioneer factor binding. Pioneer factors such as FoxA1 bind to closed regions of chromatin, expel the nucleosomes, allowing binding of a secondary factor in the absence of ATP-dependent processes. (C) Dynamic Assisted Loading. The initiating factor binds to a closed chromatin region, upon recruitment of chromatin remodeling factors the secondary factor can binding to a region previously deemed inaccessible. This is usually a bimodal switch between two TF depending on the chromatin landscape and the enhancer region. (D) The tethering model. One TF binds to a chromatin region with the secondary TF recruited upon binding or initially tether to the first TF. (E) Enhancer priming. This mechanism is functional in differentiation or dynamic assisted loading. The bound lineage-determining TF can alter the chromatin landscape by changing enhancer accessibility and histone modifications. Conversely in assisted loading the initiating factor binding actives enhancer region by increasing active histone modifications inducing the recruitment of the secondary factor to these sites. In both cases, poised enhancer state exists between the inactive and active enhancer states.