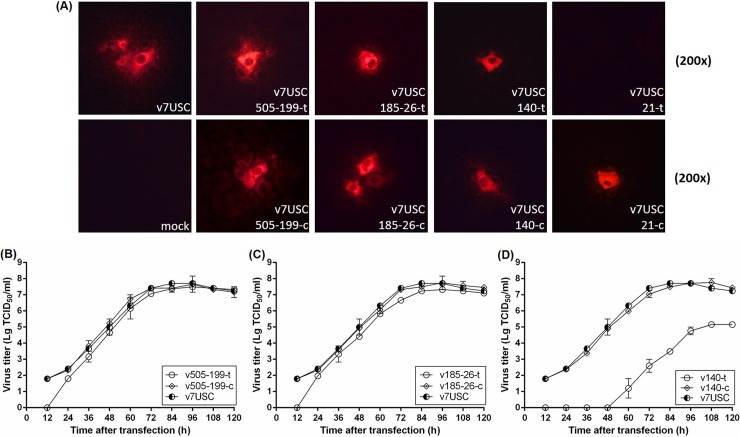
Fig 4. Mutants harboring sequences targeted by miRNAs of different abundant levels affect viral replication.
Immunofluorescence staining for intracellular N protein in mutants. A: Confluent MARC-145 cells were transfected with plasmids p505-199-t, p505-199-c, p185-26-t, p185-26-c, p140-t, p140-c, p21-t, and p21-c, as indicated respectively, with p7USC and mock-transfected cells used as controls. Cells were fixed at 24 hpt and immunostained with the mouse monoclonal SR30A antibody against the viral N protein and fluorescein isothiocyanate-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG. B: Viral growth after transfection of p7USC, p185-26-t, or p185-26-c, as representatives of moderate-abundant miRNAs. C: Viral growth after transfection of p7USC, p140-t, and p140-c, as representative of high-abundant miRNAs. D: Viral growth after transfection of p7USC, p21-140-7c, p21-140-5c, and p21-140-3c, as representatives of mutant controls of high-abundant miRNA. Viral titers were expressed as Lg TCID50/mL. Data are shown as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments.