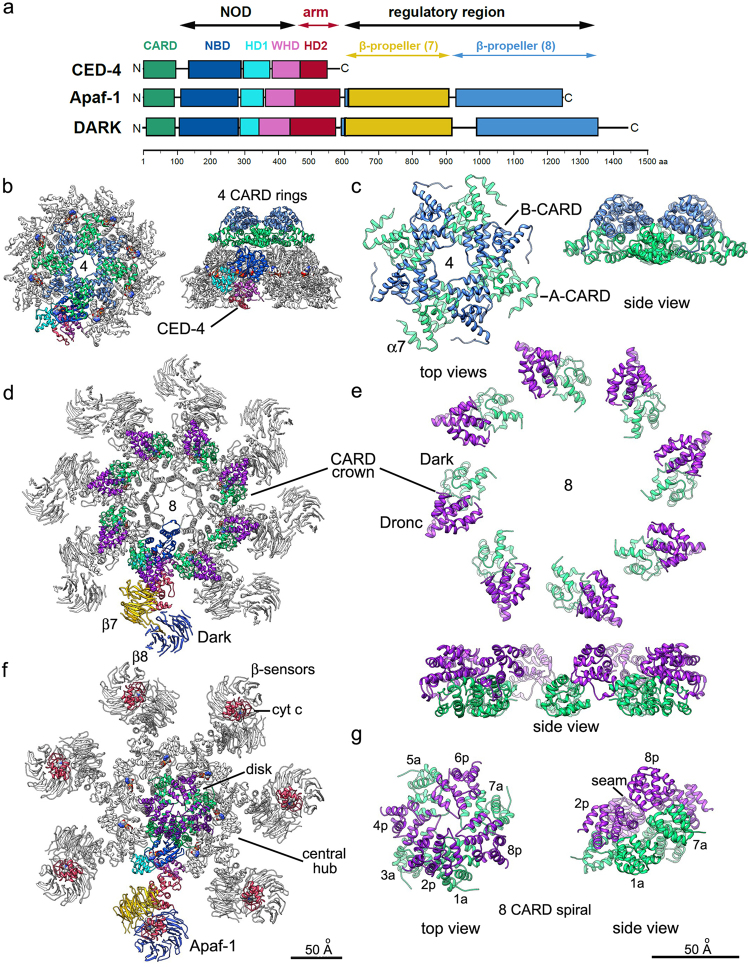
Fig. 1.
Evolutionarily conserved and divergent features of apoptosomes. a A schematic representation of C.elegans CED-4, Drosophila Dark and human Apaf-1. In Dark and Apaf-1, the last blade in the 8-blade β-propeller is formed by the HD2 linker (blue region). Protein domains are color-coded and are drawn approximately to scale. b The ground state CED-4 apoptosome is shown as a ribbon diagram with a color-coded subunit and two stacked, four CARD rings, in top and side views (PDB 3LQR). c Details of the interdigitated and stacked four CARD rings are shown with CARD-A in light green and CARD-B in blue. Linker helix 7 is marked (α7). d A top view of the Dark apoptosome is shown in a possible post-activation state (PDB 3J9K) with the Dark-Dronc CARD crown (Dronc CARD in purple). e The Dark-Dronc crown is shown at higher magnification in top and side views. f A top view of the active Apaf-1 apoptosome is shown with an 8 CARD disk (PDB 5JUY). g Top and side views are shown of the 8 CARD disk annotated with positions of Apaf-1 CARDs and pc-9 CARDs (in purple) that form a left-handed spiral for Apaf-1/pc-9 CARD pairs. Respective scale bars for b, d, f, and for c, e, g are shown