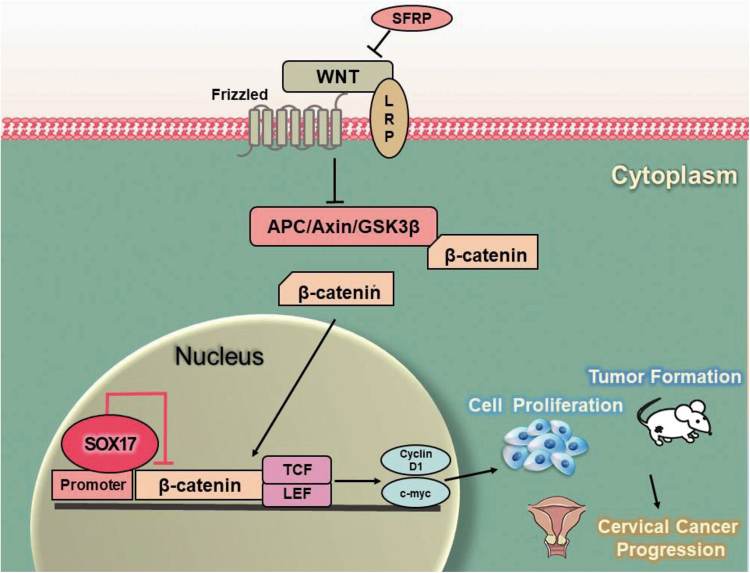
Fig. 7. Proposed model of the SOX17-mediated disruption of Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
In cervical cancer, several Wnt/β-catenin signaling antagonists including SOX17 revealed low expression because of hypermethylation. SOX17 could recognize and bind to the β-catenin promoter region as a transcription repressor and reduce the accumulation of nuclear β-catenin, leading to the down-regulation of target genes, such as cyclin D1 and c-myc. Consequently, the activity of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway was attenuated, resulting in cancer cell proliferation and tumor formation inhibition in cervical cancer cells