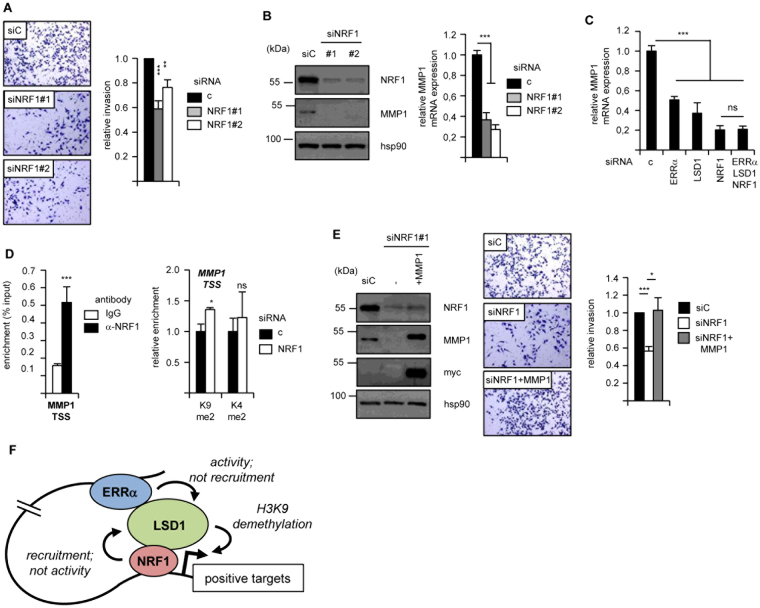
Figure 5.
NRF1 promotes cell invasion in an MMP1-dependent manner. (A) Invasion assays of MDA-MB231 cells after treatment with siNRF1. Representative fields are displayed on the left. Quantifications were performed on three independent experiments and are shown relative to control conditions. Error bars represent sem. (B) Expression of MMP1 was analyzed by Western blot (left panel; Hsp90 is used as a loading control) or RT-qPCR (right panel; expression is relative to control) after siRNA-mediated inactivation of NRF1. (C) Expression of MMP1 mRNA under the indicated single or triple KD conditions. (D) Left panel: binding of NRF1 to the MMP1 TSS analyzed by ChIP and expressed as percent input. Right panel: ChIP experiments detecting H3K9me2 or H3K4me2 at the MMP1 TSS after siRNA-mediated NRF1 depletion. Data are relative to H3 ChIP and to control conditions. (E) Left panel: expression of the indicated proteins after siNRF1 treatment and MMP1 re-introduction. Note that the myc antibody only detects the transfected myc-tagged MMP1. Right panel: Invasion assays of MDA-MB231 cells after NRF1 depletion and re-introduction of MMP1, with quantifications relative to control. Data are expressed as mean +/− sem of three independent experiments performed in triplicate. Significance are shown relative to control: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005, ns: nonsignificant. (F) Schematic representation summarizing the functional LSD1-NRF1-ERRα interactions on positive target genes. NRF1, bound at the TSS, recruits LSD1 at this location, but does not impact on its enzymatic activity. ERRα interacts with LSD1 and switches its enzymatic activity but is not responsible for its recruitment to TSSs. All three factors regulate H3K9 demethylation at the TSS in a direct (LSD1) or indirect (NRF1, ERRα) manner, resulting in gene activation.