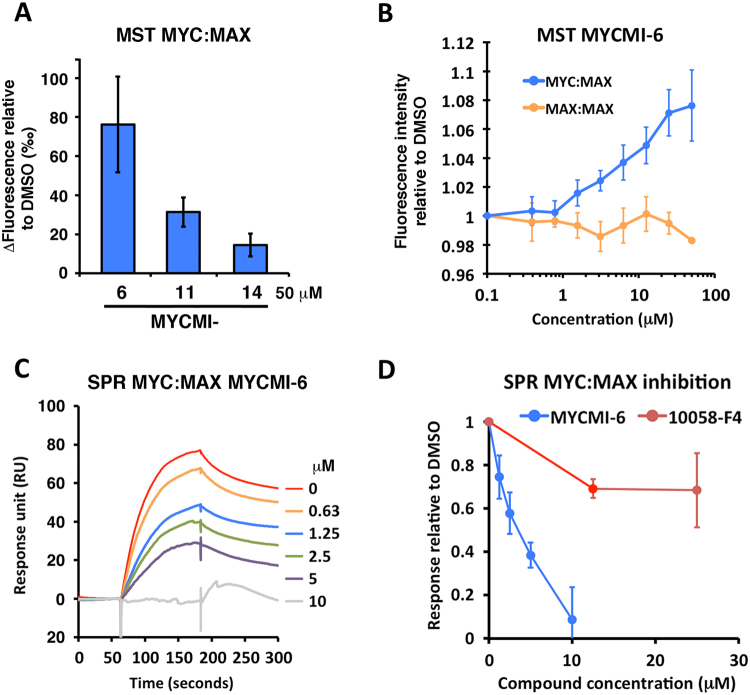
Figure 3.
MYCMI-6 inhibits the MYC:MAX bHLHZip protein interaction in vitro. (A) Microscale thermophoresis (MST) of fluorescently labeled MAX in a MYC:MAX heterodimer formation assay based on recombinant proteins. 1 µM MYCbHLHZip was pre-incubated with 50 µM of respective MYCMI before mixing with 0.5–1 µM labeled MAXbHLHZip. MST was induced and the relative changes in fluorescence (thermophoresis of labeled MAX) to DMSO were analyzed and compared. (B) MST of labeled MAXbHLHZip after titration of MYCMI-6 pre-incubated with 1 µM MYCbHLHZip, or with 1 µM MAXbHLHZip. Fluorescence intensity of labeled MAXbHLHZip relative DMSO was plotted against MYCMI-6 concentration. 3–4 experiments were carried out each with technical duplicates. (C) Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) of MYC:MAX heterodimer formation assay. MAXbHLHZip was immobilized by an amino coupling procedure to a CM5 sensor chip. MYCbHLHZip pre-incubated with or without compound (as indicated) was injected over MAX for 180 seconds, allowed to dissociate for 240 seconds and regenerated. Reference surface (without MAXbHLHZip) subtracted sensorgrams are shown from one representative experiment. (D) SPR of MYC:MAX. Binding levels of MYCbHLHZip to MAXbHLHZip were analyzed and plotted against concentration of MYCMI-6, or 10058-F4, respectively. Three experiments were carried out, respectively.