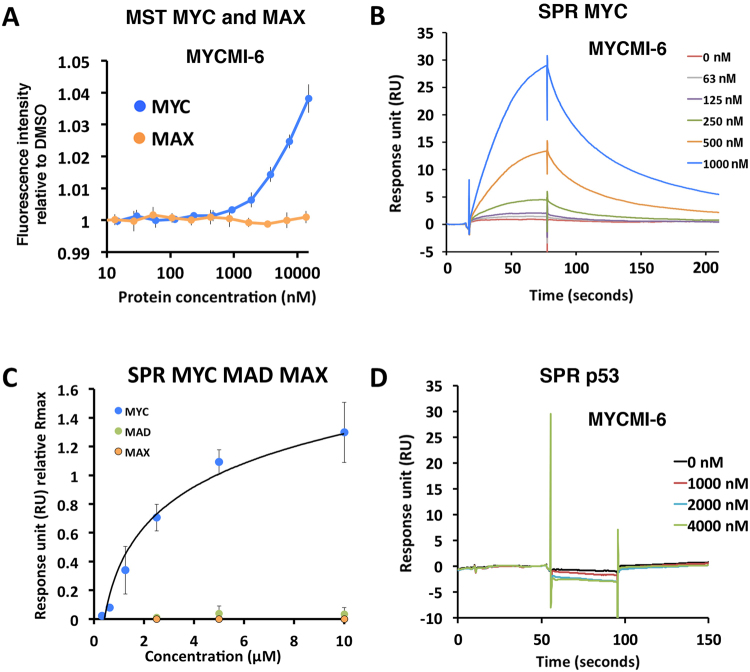
Figure 4.
MYCMI-6 binds selectively and with high affinity to the MYC bHLHZip domain. (A) MST assay measuring the effect of MYCMI-6 on MYC and MAX, respectively. Recombinant MYC bHLHZip and MAX bHLHZip proteins were titrated, respectively, in a fixed concentration (3 µM) of MYCMI-6. Changes in fluorescence were measured and normalized to control (buffer). Data are shown as mean ± standard deviation of 6–8 biological repeats. (B) SPR assay to determine the affinity of MYCMI-6 to MYC. MYC bHLHZip protein was immobilized by amino coupling on a CM5 sensor chip. MYCMI-6 was injected at various concentrations in a kinetic experiment. The reference surface was subtracted from the analyte surface to generate a sensorgram. Association and dissociation rates (ka = 9294 M−1 s−1, kd = 0.02293 s−1) were determined using the Langmuir 1:1 model in the Biacore Evaluation program fitting curves with a constant Rmax of 43 RU (theoretical Rmax), thereby suggesting a KD of 2.5 µM with a Chi2 value of 0.073. The sensorgram displays one representative experiment. Four kinetic experiments were carried out on two different sensor chips and an average KD of 1.6 ± 0.5 µM was calculated. (C) Four MYC equilibrium binding experiments with MYCMI-6 summarized in an equilibrium binding plot, carried out on two different sensor chips. Binding affinities were estimated from the plot as 50% of Rmax suggesting a KD of approximately 1.5–2 μM with an experimental Rmax of 25–30 RU (theoretical Rmax = 23 RU). SPR experiments of MYCMI-6 binding to immobilized MXD1 (MAD1) and MAX protein, respectively were included in the graph. Sensorgrams are shown in Suppl. Fig. S5A,C and D. (D) Reference subtracted sensorgram from the p53 protein SPR assay. p53 core protein was immobilized to 3000 RU and MYCMI-6 was injected at various concentrations (theoretical Rmax of 56 RU).