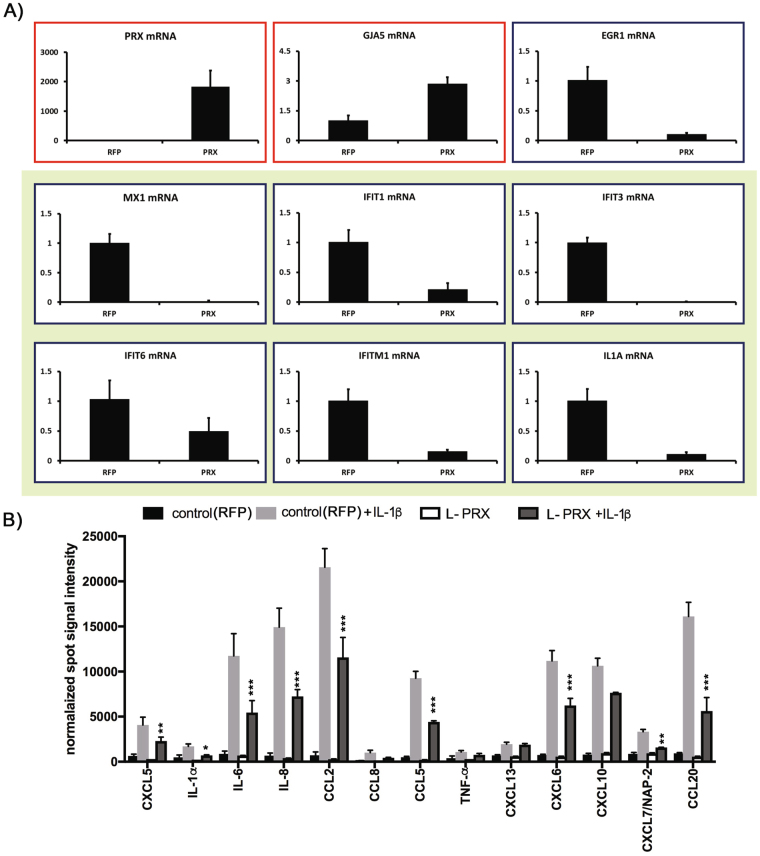
Figure 5.
Effect of PRX expression on inflammatory markers in endothelial cells. (A) Effect of PRX on inflammatory factor mRNA levels in endothelial cells. Human primary cerebral endothelial cells were infected with L-PRX viruses or RFP control viruses. After 24 hours, RNA was analyzed by quantitative RT-PCR by normalizing Ct values to 18S rRNA levels. Expression of a series of inflammatory mRNA species (green background) was significantly suppressed, as shown. Few mRNA species (red background) were upregulated. Samples were analyzed in triplicate with error bars shown as SD; all comparisons between PRX and RFP infected samples were significant with p < 0.05 (t-test). Experiments were repeated showing the same differences with three sets of cell cultures. (B) Effect of PRX on human cerebral endothelial protein expression after inflammatory challenge. We display protein array signals for human cytokines present in control (RFP-transfected cells) and L-PRX overexpressed HBMEC treated with/without IL-1β (10 ng/ml). Data represent several highly increased cytokines/chemokines in cell culture media collected at 24 hrs after introducing IL-1β. L-PRX presence in brain endothelial cells decreased expression of several proinflammatory cytokines. Values are means ± SD, n = 3; *p > 0.05, **p > 0.01, ***p > 0.001.