Fig. 1.
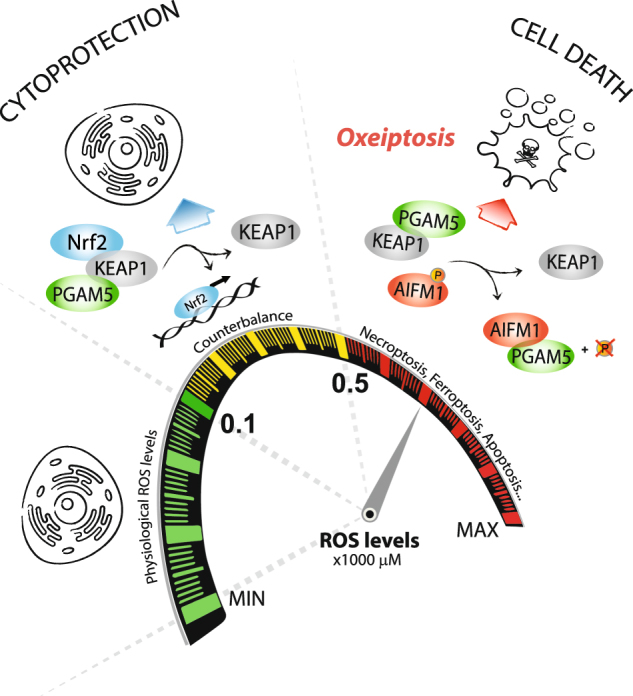
Intracellular exposure to intermediate ROS levels triggers conformational changes in KEAP1 via oxidation of its C-terminal cysteines, resulting in dissociation of the KEAP1-NRF2 complex and subsequent nuclear translocation of NRF2. In the nucleus, Nrf2 stimulates expression of cytoprotective genes that scavenge ROS. Under high intracellular ROS levels KEAP1 releases PGAM5, which binds and dephosphorylates AIFM1 at Ser116 executing a cell death program. This new signaling pathway involving KEAP1-PGAM5-AIFM1 is named oxeiptosis.
