Figure 4.
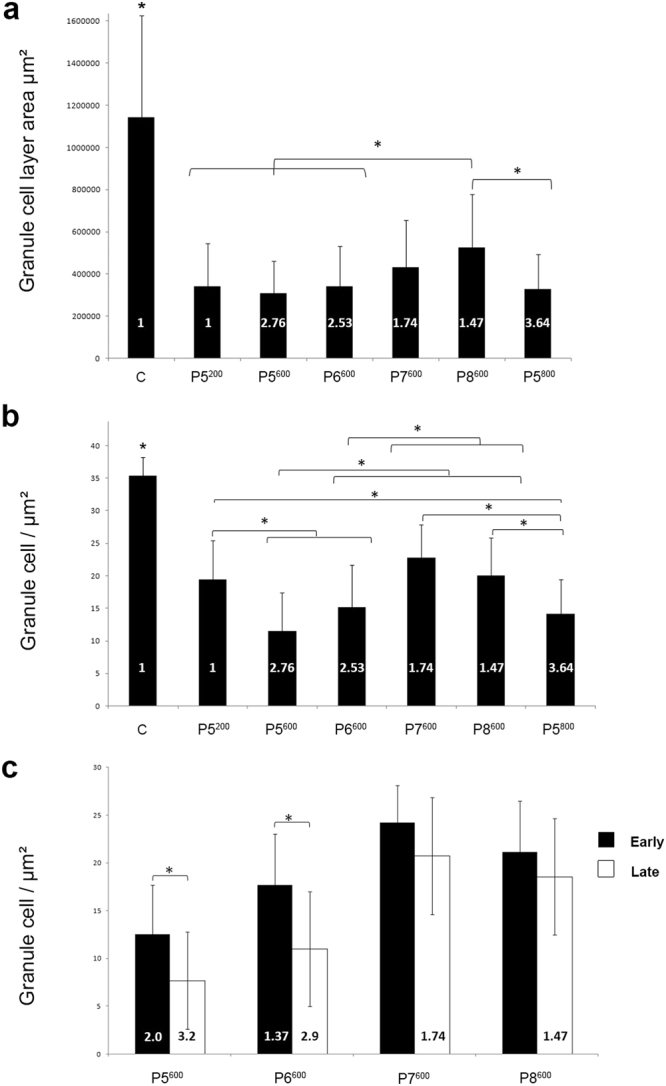
Quantitative analysis of granule cell loss in the cerebellum of postnatally X-irradiated adult rats. (a) Granule cell area is significantly reduced in the cerebellum of X-irradiated rats compared to the cerebellum of non-irradiated control rats (C). In the P8600 irradiated cerebella, granule cell loss is significantly less than in the cerebella irradiated at the critical days P5-P6 in Groups P5200, P5600, P5800 and P6600. Bars show mean ± S.D. in all graphs. (b) Granule cell density is significantly decreased in the cerebellum of all X-irradiated groups compared to the cerebellum of non-irradiated control rats (C). A significant further decrease in granule cell density is also obtained with doses above 200 rads at P5 (P5600, P5800) and P6 (P6600). A dose of 600 rads produces significantly greater granule cell loss when delivered at P5 (P5600) or P6 (P6600) than at P7 (P7600) or P8 (P8600). (c) In the cerebellum of rats irradiated with 600 rads, granule cell loss is significantly greater in the late-developing lobules VI-VIII than in the early-developing lobules IX-X after irradiation at P5 (P5600) or P6 (P6600) but not at P7 (P7600) or P8 (P8600). The values of mean index of CF innervation m are indicated within the bars. *P ≤ 0.01.
