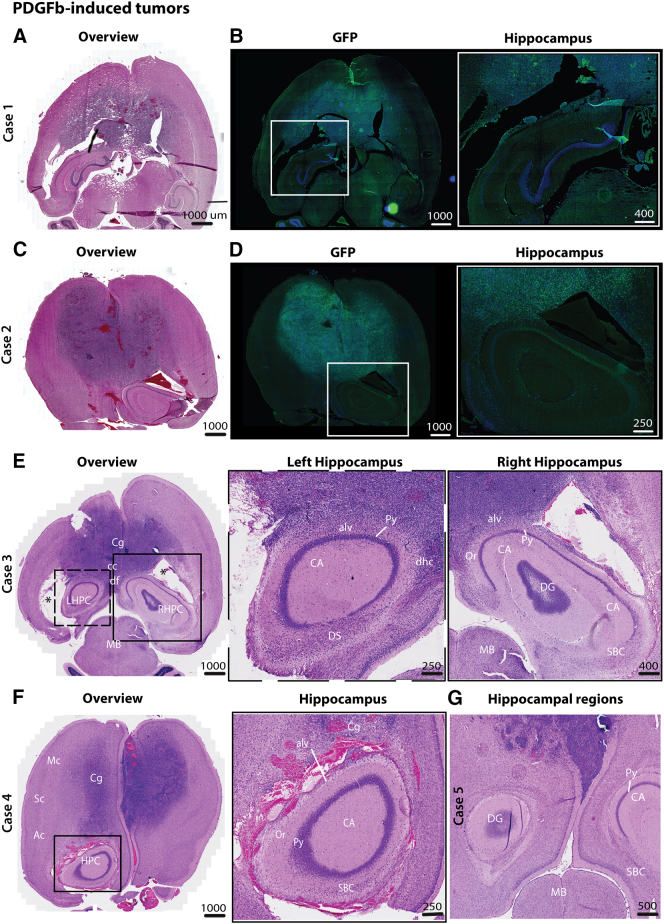
Figure 5.
Hippocampal sparing was also present in an invasive transgenic mouse GBM-model.
(A-B, C-D) HE-stained and corresponding GFP-stained axial sections of PDGF-induced tumors in cdkn2a−/− mice showed highly invasive tumors that affected both hemispheres. Tumors demonstrated widespread dissemination of tumor cells in several neo- and mesocortical regions as well as the corpus callosum. Enlarged images of the hippocampal regions showed that tumor cells extensively infiltrated the para-hippocampal regions, including cortical regions and white matter, whereas the cornu ammonis and dentate gyri appeared to be spared (inlet). A high density of tumor cells was also observed in the subependymal lining as well as in the mesencephalon. (E-G) Similar invasion patterns were observed in the other cases, and in one case, intense neovascularization was seen outside the hippocampus.
Abbreviations: Ac, auditory cortex; alv, alveus; CA, cornu ammoni; cc, corpus callosum; Cg, cingulate cortex; df, dorsal fornix; DS, dorsal subiculum; LHPC, left hippocampus; MB, midbrain; Mc, motor cortex; Oc, olfactory cortex; Or, oriens layer of the hippocampus; Py, pyramidal layer of the hippocampus; RSG, retrosplenial granular cortex; RHPC, right hippocampus; SBC, subiculum; Sc, somatosensory cortex.