Figure 2.
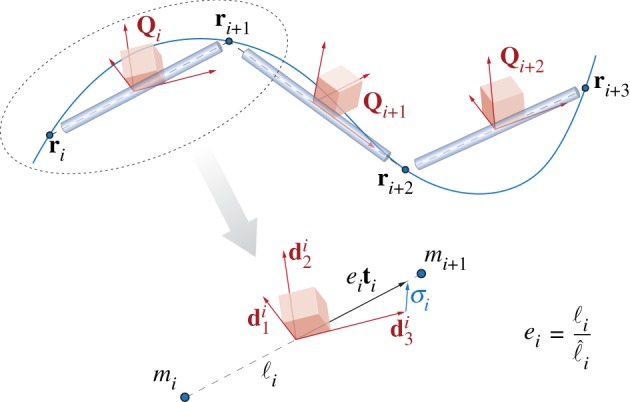
Discretization model. A discrete filament is represented through a set of vertices r(t)i=1,…,N+1 and a set of material frames . Two consecutive vertices define an edge of length ℓi along the tangent unit vector ti. The dilatation is defined as , where is the edge rest length. The vector represents the discrete shear and axial strains. The mass mr of the filament is discretized in pointwise concentrated masses at the locations ri for the purpose of advecting the vertices in time. For the evolution of Qi in time, we consider instead the mass second moment of inertia associated with the cylindrical elements depicted in blue.
