Figure 7.
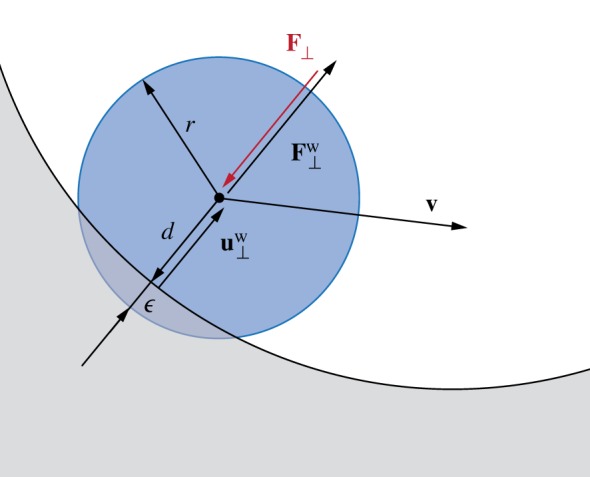
Contact model with solid boundaries. Obstacles and surfaces (grey) are modelled as soft boundaries allowing for the interpenetration ϵ=r−d with the elements of the filament (blue) characterized by radius r and distance d from the substrate. The surface normal uw⊥ determines the direction of the wall’s response Fw⊥ to contact. We note that Fw⊥ balances the sum of all forces F⊥ that push the rod against the wall, and is complemented by the other two components, which allow it to amend to possible interpenetration due to numerics. These components are an elastic one (kwϵ) and a dissipative one (γwv⋅uw⊥), where kw and γw are, respectively, the wall stiffness and dissipation coefficients.
